
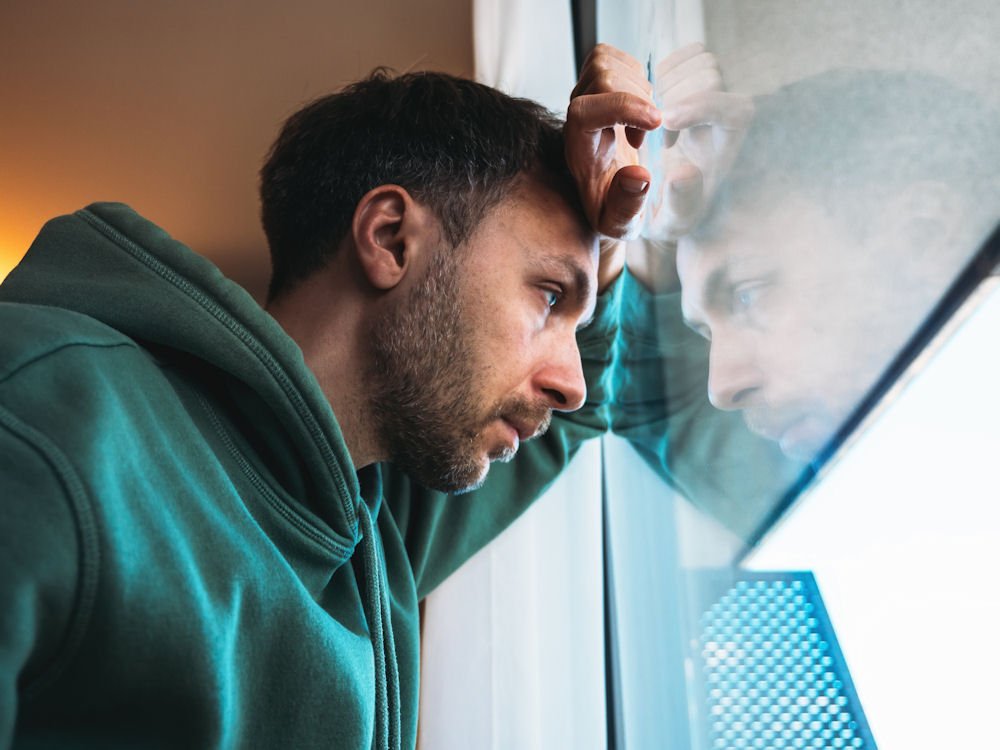
Male loneliness and addiction often go hand in hand, creating a cycle that can be difficult to break without proper understanding and support. At Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, California, we recognize how isolation affects men differently and how it can lead to substance use as a way to cope with emotional pain.
Our trauma-informed approach addresses both loneliness and addiction simultaneously, helping men rebuild meaningful connections while developing healthier coping strategies through our men’s addiction treatment program.
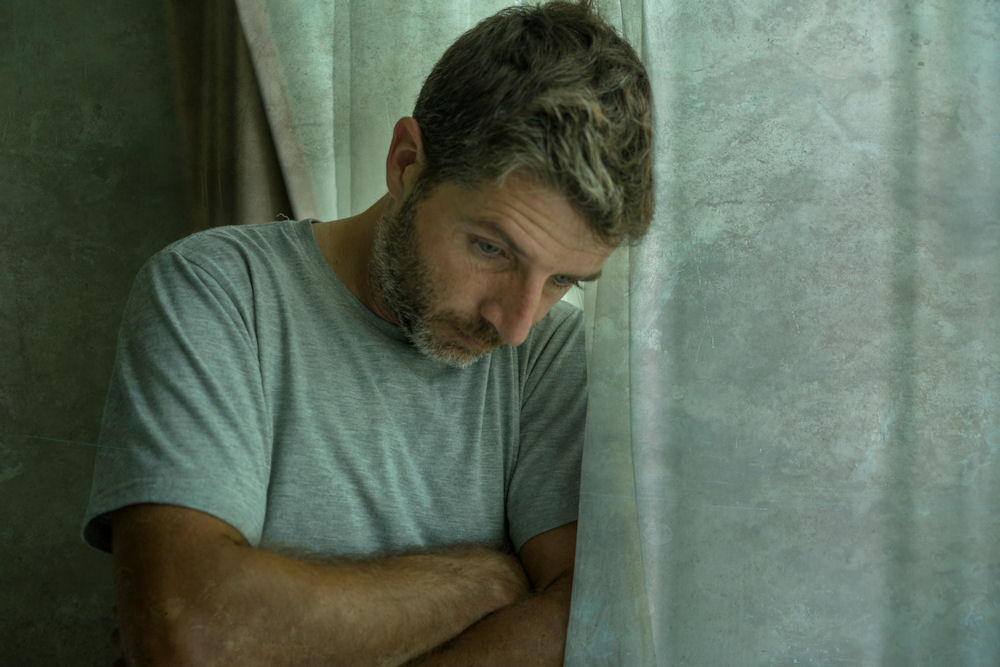
Loneliness is more than just being alone. It’s the feeling of being disconnected from others, even when people are around. For men, this experience often looks different from what it does for women. While anyone can feel lonely, men face unique challenges in recognizing and addressing these feelings.
Research conducted by the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) shows that men are less likely to admit feeling lonely or seek help for mental health and other emotional struggles. Statistics from the 2024 Gitnux MarketData Report showed that 40% of men say they feel lonely at least once a week. One in four report having no close friends, and men are less likely than women to seek help for loneliness. Additionally, 62% of men say they don’t feel comfortable sharing their emotions with friends. To distinguish male loneliness from other symptoms, signs can often appear as follows:
The difference between solitude and loneliness matters. Solitude is choosing to be alone and feeling content. Loneliness is an unwanted feeling of disconnection that causes distress. Many men experience “addiction loneliness,” which is a term describing how isolation and substance use co-occur and influence each other over time.
Men face specific social expectations that can make them more susceptible to loneliness. From an early age, many boys learn that showing emotion is a sign of weakness. Phrases like “man up” or “boys don’t cry” teach them to hide feelings rather than express them.
These masculine norms emphasize self-reliance and emotional control. While these traits can be positive in some contexts, they can also create barriers to forming deep connections. When men believe they should handle problems alone, they may avoid reaching out even when struggling with difficult emotions.
The way men typically form friendships also contributes to vulnerability. Research shows that men often build relationships through shared activities rather than personal conversations. A 2022 study in the Journal of Social and Personal Relationships found that men’s friendships tend to focus on doing things together rather than discussing emotions. This can limit opportunities for emotional support during difficult times. Cultural factors that increase male isolation include:
These patterns don’t mean men are incapable of connection. Rather, they highlight how social messages shape behavior and influence men’s mental health crisis.
Loneliness and addiction often feed into each other, creating what experts call “addiction loneliness.” This describes how emotional isolation can lead to substance use, and how substance use can deepen isolation.
When someone feels lonely, their brain chemistry changes. The National Institute on Drug Abuse explains that chronic loneliness increases stress hormones like cortisol while reducing feel-good chemicals like dopamine and oxytocin. These changes create feelings similar to physical pain and can trigger cravings for relief.
Substances temporarily alter this brain chemistry. Alcohol, opioids, and other drugs provide a quick boost of dopamine, briefly easing emotional distress. However, this relief doesn’t last. Over time, the brain adapts, making it harder to feel pleasure naturally. This can lead to increased substance use and further isolation. The cycle typically works like this:
A 2023 study published in the Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment found that individuals reporting high levels of loneliness were 2.5 times more likely to develop substance use disorders than those with strong social connections. The same research showed that addressing social isolation improved treatment outcomes by up to 40%.
From a brain perspective, both loneliness and addiction affect the same reward pathways. Chronic isolation reduces sensitivity to natural rewards like social interaction or hobbies. This makes substance-induced rewards feel more powerful by comparison, increasing vulnerability to dependence.

Recognizing when loneliness is leading to problematic substance use can help with early intervention. The signs often develop gradually, becoming more noticeable over time.
Early warning signs include:
As the connection between loneliness and addiction strengthens, more serious signs may appear:
Research from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration shows that men are more likely than women to use substances as a way to manage difficult emotions, indicating a growing need for addiction counseling in Marin County. A 2022 study found that men were 30% less likely to seek help for emotional distress but 40% more likely to report using alcohol or drugs to cope with stress.
These patterns can be especially pronounced in men who have experienced trauma or major life transitions like divorce, job loss, or retirement, often benefiting from PTSD and addiction treatment tailored to address both issues. During these periods, existing support networks may change or disappear, increasing vulnerability to both loneliness and substance use.
The combination of loneliness and addiction can significantly impact both physical and mental health. Each condition alone presents health risks, but together they can create more severe and complex problems.
Physically, chronic loneliness activates the body’s stress response. According to research from the National Institute on Aging, this can lead to inflammation, weakened immunity, and increased risk for cardiovascular disease. A 2021 study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that people experiencing persistent loneliness had a 29% higher risk of heart disease and a 32% increased risk of stroke.
Addiction adds additional physical health risks:
The mental health impact is equally significant. Loneliness is strongly associated with depression and anxiety. The Centers for Disease Control reports that social isolation increases the risk of depression by 50% and anxiety disorders by 45%. When combined with substance use disorders, these risks often require addiction and depression treatment to address both conditions effectively. Common mental health effects include:
The National Institute on Drug Abuse notes that approximately 50% of individuals with substance use disorders also experience mental health conditions. This rate is even higher among those reporting significant loneliness, highlighting how these factors compound each other’s effects.

Addressing male loneliness and addiction requires approaches that recognize how these issues connect. Recovery involves both healing relationships and developing healthier coping strategies.
Creating authentic relationships starts with small, consistent steps. For many men, activity-based connections feel more comfortable than conversation-focused ones. Joining groups centered around shared interests provides natural opportunities for connection without pressure. Effective ways to build connection include:
Learning to be vulnerable takes practice. Many men find it helpful to start by sharing smaller concerns before discussing deeper feelings. Having even one person who listens without judgment can make a significant difference in reducing loneliness.
Several evidence-based therapies effectively address both loneliness and addiction:
At Golden Gate Recovery, we combine these approaches with male-specific programming that addresses the unique ways men experience loneliness and addiction. Our treatment includes individual counseling, group sessions, and practical skill-building activities that support long-term recovery.
Clients can expect a supportive environment that respects men's communication styles while encouraging emotional growth. Treatment typically includes education about addiction, practice with healthy coping skills, and opportunities to build supportive relationships with peers who understand similar struggles.
Recovery involves learning new ways to manage difficult emotions without substances. Effective coping strategies include:
These skills take time to develop. Many men find it helpful to work with a counselor or recovery coach who can provide guidance and accountability during this learning process.
When someone you care about is dealing with loneliness and addiction, your approach can make a difference in their willingness to seek help. Understanding how men typically communicate about emotional difficulties helps create more effective support. Helpful communication strategies include:
Setting clear boundaries protects both you and the person you’re supporting. This means being clear about what help you can offer while avoiding enabling behaviors that maintain the addiction.
Examples of healthy boundaries include:
Connecting someone to resources often works best when presented as information rather than directives. Having options allows the person to maintain a sense of control in the decision-making process.
Recovery from the combination of loneliness and addiction happens gradually. It begins with recognizing how these issues reinforce each other and taking small steps toward change.
The early recovery period focuses on physical stabilization and learning basic coping skills. This typically takes several weeks to months. During this time, individuals begin to identify patterns in their substance use and practice new responses to emotional triggers.
As recovery progresses, the focus shifts to deeper emotional healing and relationship building. This middle phase often involves addressing past hurts, practicing vulnerability in safe relationships, and developing a stronger sense of identity beyond addiction. This process usually spans several months to a year.
Long-term recovery involves integrating these changes into everyday life. This includes building a supportive community, finding meaning and purpose, and continuing to develop emotional resilience. While this process continues throughout life, many people report significant improvements in their sense of connection within 1-2 years of beginning recovery.
Connection plays a crucial role throughout this journey. Research consistently shows that strong social support improves recovery outcomes. A 2023 study in the Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment found that individuals with supportive relationships were 40% more likely to maintain long-term sobriety than those who remained socially isolated.
At Golden Gate Recovery, we’ve seen how addressing male loneliness as part of addiction treatment leads to more sustainable recovery. Our programs create spaces where men can practice authentic connection while developing the skills needed for lasting change.

Male loneliness often involves emotional isolation despite potential social contact, while women may maintain emotional connections but still feel misunderstood or unsupported in those relationships.
Yes, loneliness alone can lead to addiction by creating emotional distress that a person might try to relieve through substance use, even without other mental health conditions.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, group therapy, and trauma-informed approaches are particularly effective because they address both relationship patterns and substance use behaviors simultaneously.
Recovery timelines vary widely, but most people see significant improvements in their sense of connection within 6-12 months of consistent treatment and practice with new relationship skills.
Yes, many communities offer men's recovery groups, and some treatment programs provide male-specific programming that addresses both substance use and connection challenges.
If you or someone you care about is struggling with loneliness and addiction, we’re here to help. At Golden Gate Recovery, we understand the unique challenges men face when dealing with these interconnected issues. Our comprehensive approach addresses both the addiction and the underlying loneliness that often drives it. Contact us today to learn more about our programs and how we can support your journey toward healing and connection.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

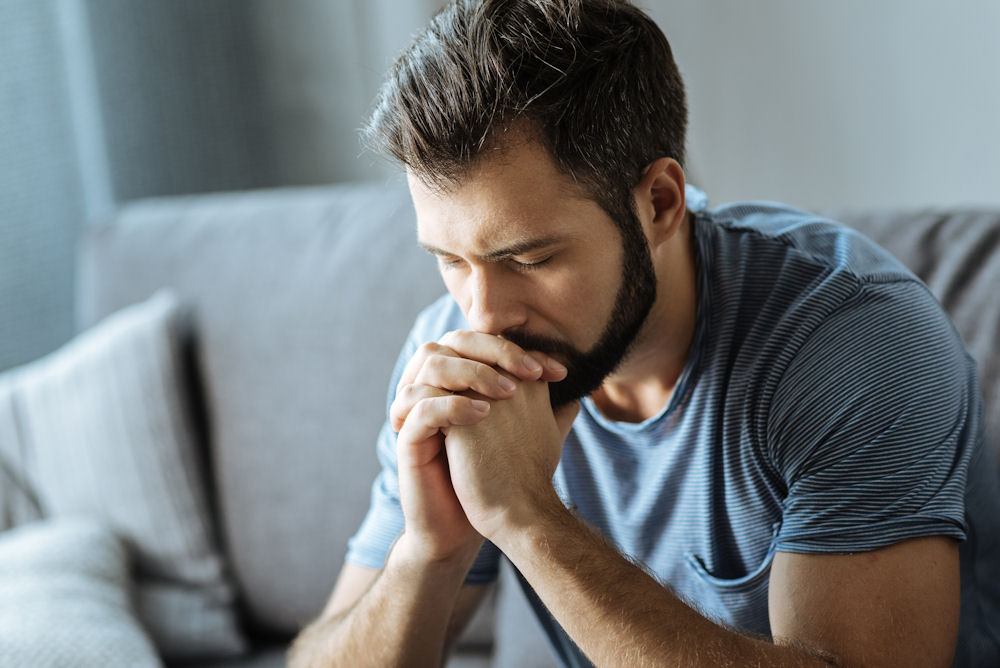
The men’s mental health crisis is an ever-increasing, often silent problem. Silent in the sense that an overwhelming number of men conceal these battles. Sadly, the unfair and untrue stigma surrounding men and mental health is the reason many men opt to suffer in silence.
However, bottling these troubles inflicts deeper emotional, mental, and physical stress that ends up manifesting itself in self-harming ways. In honor of May’s Mental Health Awareness Month, here are important details to watch for, including symptoms, risks, and challenges.
Someone may have a mental health struggle and not even know it. Please be aware and seek help if you or a loved one exhibits any or all of the following symptoms.
Mental health conditions are usually accompanied by sudden mood swings that can change on a dime for seemingly no reason. Many personality, anxiety, and depression disorders have very specific triggers that can turn a good mood into a bad one. It’s important to take notice of anyone, including yourself, whose countenance disturbingly shifts without any apparent rhyme or reason. If this characteristic describes you or someone you love, seek professional assessment to get a proper diagnosis.
This symptom is especially severe and should not go unchecked without seeking immediate treatment. Any brief or extended ponderings of suicidal thoughts should be met with swift and immediate action. We can help you reverse these harmful thought processes through personalized mental health training. Thanks to our unparalleled mental health experts, you don’t have to suffer the suicidal tug-of-war with these harmful thought cycles.
Separate from suicidal thoughts or tendencies, feelings or thoughts of hopelessness is the preeminent thought or feeling that can ultimately lead to suicidal tendencies. Once any feeling of hopelessness or depression arises, it’s important to treat this before it progresses into suicidal tendencies. Getting help at this stage of your mental health struggle maximizes efficacy potential and therapeutic responsiveness.
If you or a loved one exhibits anxiety symptoms or paranoia semi-frequently, it may be indicative of a mental illness. Other indications of high anxiety levels include mild to severe involuntary tremors, high blood pressure, and heart rate. Eventually, such symptoms and mental health conditions will lead to physical health issues like cardiovascular or respiratory problems if left untreated. Don’t let elevated stress levels and anxiety disorders take a toll on your mental and physical health. Reach out to us now to get immediate symptom relief
If you or a loved one is easily angered over minor infractions, it may be a deep-rooted mental condition. The individual may even recognize their anger problem and not understand the root cause, making it even more frustrating. We have the answers to your frustrations. Our treatment team will help you identify the root of your irritability and help you effectively deal with the underlying cause.

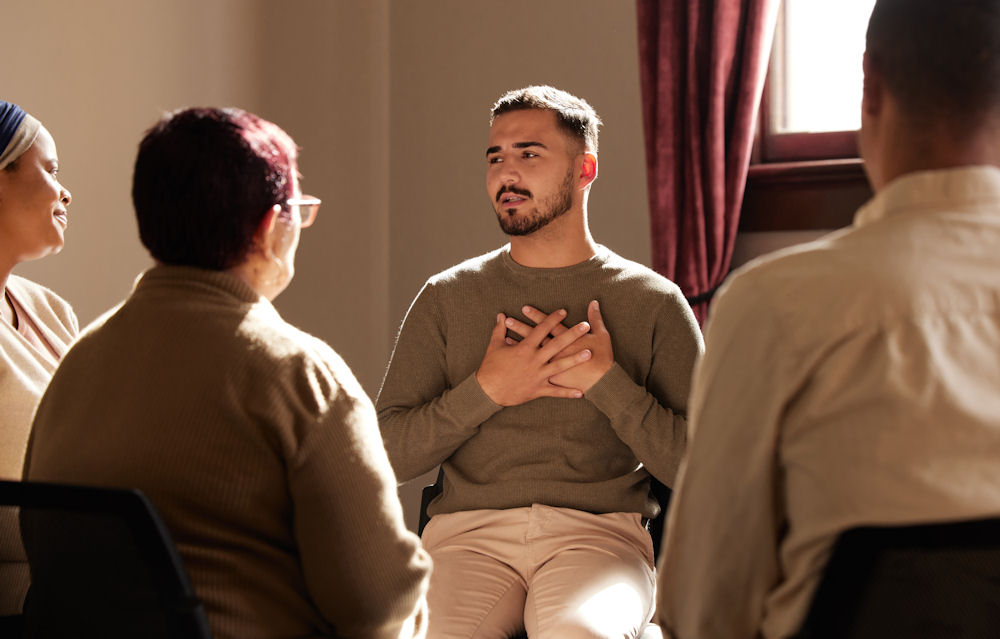
There are different challenges men face than women due to gender-based discrepancies in treatment approaches, focuses, and public reception. Golden Gate Recovery places a strong emphasis on meeting all of the following challenges through our revolutionary treatment methods.
A primary contributor to the men’s mental health crisis revolves around the stigma challenges men face in treatment. Stigma suggests that ‘real’ men can handle their challenges without external help, and any failure to do so is less “manly”. Not only is this untrue, but the opposite is true. It takes a truly strong man to accept help for mental health challenges that are outside of their control.
Unlike their female counterparts, Male mental health patients often find it more difficult to open up. It’s especially difficult to open up to a therapist they don’t know when they have a hard enough time opening up to loved ones. We break these communication barriers by getting to know our patients on a personal level without judgment. We encourage, we motivate, and we empathize with your needs with the utmost sincerity.
Statistics conclude that males above the age of 12 turn to substances at almost double the rate of females in the same age bracket. In terms of mental health coping mechanisms, it’s very common for men to cope with such issues through substance abuse. Many who enter mental health therapy also have co-occurring substance use disorders. In such cases, dual-diagnosis therapy is the best option for people struggling with co-occurring mental and addiction disorders.
This point is so much more than an inability to open up. Some men can be so overly hard on themselves to the point where they feel accepting help equals weakness. On the contrary, as alluded to earlier, admitting you need help is the strongest decision you can make. Unfortunately, the perception of what’s tough and what isn’t has been stigmatized, preventing many men from getting proper treatment.
Statistics confirm that men are less likely to seek the treatment they need than their female counterparts. This adds additional challenges with men refusing to seek therapy stemming from what they deem as threats to their masculinity. The reason for these self-preventing hurdles includes, but is not limited to, pride, lack of self-esteem, or shame in recovery. Most dangerously, the individual may even be in denial that they need help due to the aforementioned factors.

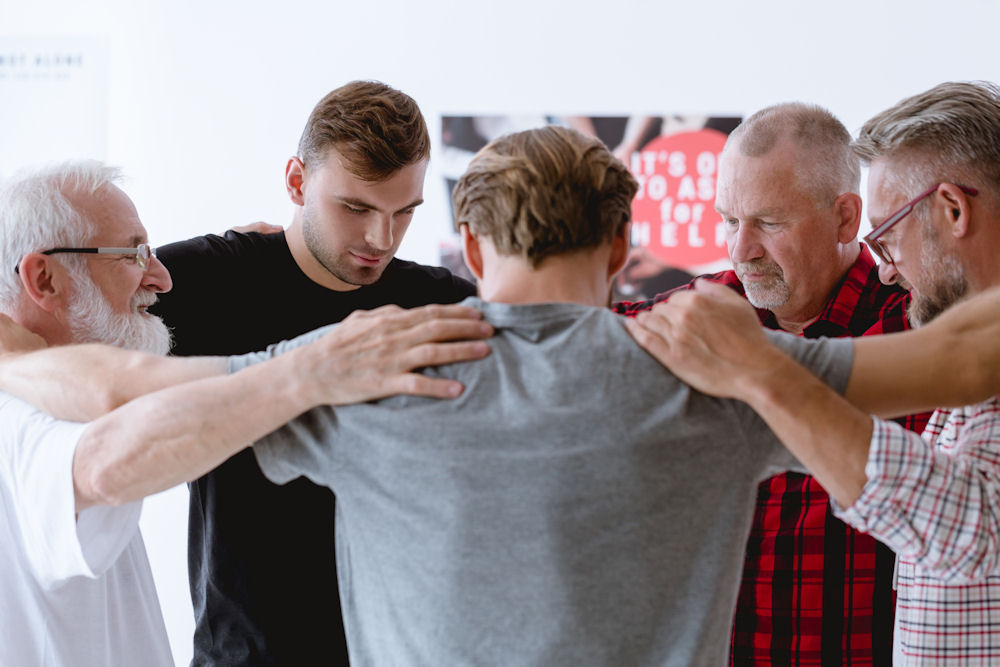
Studies find there are specific mental health conditions that men are more prone to than others. Seek a mental health assessment to diagnose any of the following common mental health conditions.
Addiction is more than a behavior or habit. It’s an official mental health condition that alters the mind’s genetic makeup. As we touched on earlier, men are more likely to turn to addictive substances as a coping mechanism. This is the case not just for mental health problems, but for other hardships as well. The only way to repair these addiction-induced mental imbalances is to get professional therapy.
Though researchers find a greater percentage of women suffer depression than men, a staggering 80 percent of suicides are reportedly male. This is a troubling revelation of the dire state of the men’s mental health crisis and the failing level of care. These suicide discrepancies, despite having significantly lower depression rates, are due to a lack of therapeutic attentiveness and men suffering silently. In light of May’s Mental Health Awareness Month, it’s important to encourage men with mental problems to share their struggles.
Personality disorders like bipolar disorder, PTSD, OCD, and others are very prevalent among men. In addition, any underlying childhood, adult, or current trauma exacerbates the risk of acquiring these personality disorders. The worst part is that, since men are more unlikely to seek help, many of these conditions remain undiagnosed and undocumented. Our treatment team is standing by to help you diagnose and pave your most effective personalized road to mental healing.

A variety of gender-specific approaches are necessary since men and women think and respond differently to various treatment methods. Depending on your condition and needs, a specialist will place you in any of the following programs based on your assessment results.
Curbing the men’s mental health crisis in the world begins with you. We understand the unique challenges men face. It’s the reason we lead the charge in attacking the men’s mental health crisis that has become a global epidemic.
We exert our greatest efforts, tools, and top-quality tactics to ensure men get the most attentive and thorough care they deserve. You’ll be one of the many who’ve found mental healing made possible by our thorough treatment methods. Reach out today to find your healing solution.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Does vitamin D deficiency cause depression? Research suggests a possible link between low vitamin D levels and mood disorders. Many people struggle with depression, and addressing potential deficiencies may help improve mental well-being.
Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, California, provides support for those facing these challenges, offering guidance on overall health in recovery. Exploring the connection between vitamin D and mental health could be a step toward feeling better.
Vitamin D is a nutrient that helps keep the body healthy. It supports bone strength, immune function, and even brain health. People get vitamin D from sunlight, food, and supplements. Without enough, the body may not work as well as it should.
Depression is a mental health condition that affects mood, energy, and daily life. It can cause sadness, fatigue, and trouble concentrating. Many factors contribute to depression, including genetics, stress, and overall health.
Some experts believe there’s a connection between vitamin D and depression. Since vitamin D affects brain function, low levels might impact mood. This leads to an important question: Does vitamin D deficiency cause depression? While research is ongoing, studies suggest it may increase the risk of depressive symptoms.

Vitamin D is important for overall health. It helps the body absorb calcium, supports the immune system, and plays a role in brain function. People get vitamin D from sunlight, certain foods, and supplements. Without enough, the body may not function at its best.
Mental health affects thoughts, emotions, and daily life. Mental health helps people handle stress, build relationships, and stay motivated. Depression, anxiety, and mood disorders can make daily tasks feel overwhelming. Many factors influence mental health, including genetics, lifestyle, and nutrition.
Some researchers believe vitamin D affects mental well-being. Since it helps regulate brain chemicals, low levels might contribute to mood issues. This raises an important question: Does vitamin D deficiency cause depression? Studies suggest low vitamin D levels may increase the risk of depressive symptoms. While it’s not the only factor, it could play a role.

Vitamin D plays a role in how the brain functions. It helps produce chemicals like serotonin and dopamine, which affect mood and emotions. When vitamin D levels are low, the brain may not regulate these chemicals properly, leading to mood changes.
Many people wonder, does vitamin D deficiency cause depression? While it’s not the only factor, some studies suggest low levels may contribute to depressive symptoms. People with vitamin D deficiency often report feeling tired, unmotivated, or emotionally drained.
Seasonal depression is another example of this connection. In the winter, when sunlight exposure is limited, some people experience mood changes. This may be due to lower vitamin D levels during colder months.
Improving vitamin D levels could help support mental well-being. Spending time in the sun, eating vitamin D-rich foods, and taking supplements may help. A doctor can help determine if a deficiency is affecting your mood. Small changes in daily habits could make a difference.
Vitamin D deficiency can happen for many reasons. Some people don’t get enough sunlight, while others have trouble absorbing it from food. Since vitamin D supports brain function, low levels may affect mood. This leads to the question: does vitamin D deficiency cause depression? While it’s not the only factor, certain risks can make a deficiency more likely.

Vitamin D deficiency and depression can share similar symptoms, making it hard to tell them apart. Is this the reason it is believed that vitamin D deficiency causes depression? While research is still ongoing, low levels may contribute to certain mental and physical symptoms.
Vitamin D plays a big role in brain health. It helps regulate neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which affect mood and emotions. When vitamin D levels are low, these chemicals may become imbalanced, leading to mood changes, fatigue, and mental fog.
Brain receptors for vitamin D help protect nerve cells. This vitamin supports brain plasticity, which allows the brain to adapt and function properly. Some studies suggest that low levels may be linked to cognitive decline and memory issues.
Vitamin D also plays a role in reducing inflammation in the brain. It has anti-inflammatory properties that help keep the brain’s function intact. A deficiency can lead to increased brain inflammation, which may affect concentration and cause mood swings.
Without enough vitamin D, the brain may struggle to maintain mental clarity and emotional balance. This can make it harder to manage stress, focus on tasks, or feel motivated. Regular exposure to sunlight, eating vitamin D-rich foods, and taking supplements may help keep levels in check. What are Some Natural Ways to Increase Vitamin D Levels?
There are several natural ways to boost vitamin D levels. Sunlight is one of the best sources. Just 10 to 30 minutes a day of direct sun exposure can help your body produce vitamin D. The amount of time you need depends on skin tone, geographic location, and the season.
Eating vitamin D-rich foods is another way to increase levels. Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are great sources. Fortified foods such as milk, orange juice, and breakfast cereals can also help you meet your daily needs.
For those who prefer plant-based sources, eggs and mushrooms are good options. Some mushrooms, like shiitake and maitake, naturally contain vitamin D, especially when exposed to sunlight.
If getting enough vitamin D from food or sunlight is challenging, vitamin D supplements can be a helpful alternative. It’s important to follow the recommended dosage to avoid taking too much, as excess vitamin D can lead to health issues.

When treating vitamin D deficiency and depression, it’s important to focus on both diet and supplementation. The amount of vitamin D you need depends on various factors, such as age, health, and location. Most adults need about 600 to 800 IU per day, but some may need more, especially if they have a deficiency.
If you’re wondering how much vitamin D to take for depression, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider. They can recommend the right dosage based on your specific needs and vitamin D levels. Some studies suggest higher doses, like 1,000 to 2,000 IU per day, may help improve mood and energy levels in people with low vitamin D.
Sun exposure and vitamin D-rich foods are also part of the solution. While supplements can help, they should be used in conjunction with other healthy habits, such as exercise and proper nutrition.
At Golden Gate Recovery, we understand the unique challenges men face on the road to recovery. Our Men’s Rehab Center offers a safe, supportive environment where you can focus on healing. Whether you’re struggling with addiction, mental health issues, or both, we’re here to help you regain control of your life.
We use evidence-based therapies to address the root causes of addiction and mental health concerns. This approach allows us to support you in achieving long-term recovery.
We value the strength of community and connection. At Golden Gate Recovery, you’ll find a team that truly cares about your well-being. Together, we’ll help you rebuild your life, step by step.
If you’re ready to make a change, reach out to us today. Our Men’s Rehab Center is here to guide you on your journey to a brighter future. Contact us now to learn more and take the first step toward lasting recovery.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Let’s talk about breaking the stigma—because it’s long overdue, especially when it comes to mental illness and the LGBTQ+ community. Too often, the stigma around mental health makes it harder for LGBTQ+ individuals to live authentically and get the support they deserve. It shows up in all kinds of ways—everyday misunderstandings, harmful stereotypes, and even outright discrimination.
But here’s the thing: change starts with all of us. By educating ourselves, encouraging better connections between clinicians and LGBTQ+ patients, and creating safe spaces for people to share their stories, we can take steps toward a more supportive, understanding world.
Mental illness stigma is real, especially affecting LGBTQ individuals and other minority groups. At Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, California, our men’s only rehab center are allies of the LGBTQ+ community. We specialize in addressing the needs and barriers that affect males from getting the treatment they need through our LGBTQ mental health services.
Men’s mental health stigma is a deeply rooted issue that affects countless individuals, especially LGBTQ+ men. Society still clings to outdated ideas of masculinity, expecting men to be strong, stoic, and self-reliant. These pressures make it hard for any man to admit they’re struggling, but for LGBTQ+ men, the challenges are even greater.
Alongside societal expectations, they often face homophobia, transphobia, and other forms of discrimination, which compound the difficulty of seeking help. The result? Many LGBTQ+ men suffer in silence, with mental health issues such as anxiety disorders and depressive disorders left unaddressed.
Mental illness stigma manifests in both subtle and overt ways. Dismissive comments, such as “just man up,” can undermine a person’s willingness to seek help. Additionally, LGBTQ+ men may feel isolated if healthcare providers fail to understand their unique experiences. The impacts of stigma and discrimination are far-reaching, often leaving lasting emotional and psychological scars. Some key effects include:
By understanding these impacts, we can work to create more supportive environments and break the cycle of stigma and discrimination.

It’s no secret that the relationship between a patient and clinician is key to effective care. For LGBTQ+ individuals, a lack of cultural competency or empathy from clinicians can create an uncomfortable, even harmful, experience. On the flip side, patients may feel too afraid of being judged to open up about their mental health struggles fully. Clinicians can help break down these barriers and foster a more trusting and supportive relationship by:
Take the time to deeply understand LGBTQ+ issues, including the effects of mental illness stigma, systemic discrimination, and the unique challenges faced by different identities within the community. This involves ongoing training, reading current research, and seeking input from LGBTQ+ voices.
A welcoming practice goes beyond appearances. Ensure your space feels safe through visible signs of inclusion, like LGBTQ+ affirming materials, but also through policies that make it clear you prioritize respect and equity for all patients.
Encourage patients to share their stories by being genuinely curious and open. Avoid assumptions and show empathy by actively listening to what they are comfortable disclosing.
Words matter. Using the correct pronouns, affirming terms, and respectful language demonstrates care and validates a patient’s identity. Consistently practicing inclusive communication builds trust and shows that their experiences are valued.

Depression among LGBTQ+ youth is a growing concern. Studies consistently show that LGBTQ+ young people experience higher rates of depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation than their heterosexual and cisgender peers. Mental illness stigma, combined with societal rejection, puts this group at significant risk. Here are the contributing factors:
LGBTQ+ youth often face harassment in school and even rejection from their families. This rejection can take an emotional toll, leaving young people feeling isolated and unsupported.
Feeling unseen in the media or society can contribute to a sense of invisibility. When LGBTQ+ youth don’t see their identities positively reflected, it reinforces feelings of otherness and loneliness.
Many LGBTQ+ youth live in areas where mental health services are either unavailable or fail to affirm their identities. Even when care is accessible, it’s often not culturally competent, further discouraging youth from seeking help.
Support must begin at home, extend into schools, and thrive within communities. Creating inclusive environments, providing access to LGBTQ+-affirming therapy, and fostering opportunities for self-expression can transform the mental health landscape for these young individuals and give them the support they deserve.

While discrimination and stigma are closely connected, they represent distinct challenges that require different approaches to address effectively. Stigma is rooted in negative societal attitudes, such as stereotypes about LGBTQ+ individuals or shaming those with mental health issues. These beliefs often paint people as “less than” or incapable, perpetuating harmful narratives. Discrimination, on the other hand, goes beyond attitudes and involves concrete actions or policies that treat individuals unfairly based on these biases.
For example, stigma might involve the widespread assumption that LGBTQ+ individuals cannot build healthy, lasting relationships. Discrimination occurs when such attitudes translate into actions, such as denying LGBTQ+ couples the legal right to marry or preventing them from adopting children. While stigma creates the foundation of harmful perceptions, discrimination enforces these beliefs through societal systems and policies.
Addressing both requires a dual approach. Shifting societal attitudes through education, media representation, and advocacy can help dismantle stigma. At the same time, enforcing inclusive laws and policies is critical to protecting individuals from discrimination and ensuring equity. Together, these efforts can foster a world where LGBTQ+ individuals and those with mental health struggles feel valued, respected, and empowered to thrive.

The most empowering thing clinicians can do is let LGBTQ+ patients lead the conversation about their mental health. Each person’s experience is deeply personal, shaped by their unique challenges, strengths, and history. By acknowledging this, clinicians can foster trust and create a more meaningful therapeutic relationship.
Clinicians can achieve this by adopting a strength-based approach. Instead of focusing solely on the struggles a patient has faced, emphasize their resilience, coping strategies, and the progress they have made. This not only builds confidence but also empowers patients to see themselves as capable of overcoming difficulties. For example, a clinician might say, "You’ve faced some incredibly tough situations, yet you’ve found ways to keep going—let’s explore how you’ve done that."
Open-ended questions are another vital tool. These encourage patients to share their stories in their own words, providing insights into their needs and priorities. Questions like, "Can you tell me more about how this has affected your daily life?" or "What feels most important for us to focus on today?" show a willingness to listen without assumptions.
Respecting boundaries is equally essential. Some topics may feel too raw or personal for a patient to discuss immediately. Clinicians should be attuned to verbal and nonverbal cues, ensuring patients feel safe and supported rather than pressured. For instance, if a patient hesitates to discuss family dynamics, a clinician could say, "We can come back to this whenever you feel ready."
In practice, trusting patients to guide the conversation about their lives creates an environment where they feel seen, heard, and valued. This patient-led approach enhances the therapeutic alliance and encourages long-term engagement with mental health care, paving the way for meaningful progress and healing.
Being an ally to LGBTQ+ patients goes beyond good intentions—it’s about taking meaningful action to create an inclusive healthcare environment. Clinicians can improve the experience for LGBTQ+ individuals by actively supporting their well-being and fostering trust.
Actionable Steps:
By taking these steps, clinicians can foster a supportive and inclusive healthcare environment for LGBTQ+ patients.

At Golden Gate Recovery, we proudly stand as a trusted ally to the LGBTQ+ community. We are dedicated to providing compassionate, affirming care that acknowledges the impact of mental illness stigma.
Our trained team ensures every patient feels respected and supported, creating personalized treatment plans for each individual’s unique journey. Through partnerships with local LGBTQ+ organizations, we connect patients to vital resources and support systems.We are committed to breaking down barriers, challenging stigma, and fostering a safe space where LGBTQ+ individuals feel valued. Contact us today.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

The holiday season is often portrayed as a time of joy and togetherness, but for many of us, it also magnifies grief. The absence of loved ones can feel especially heavy during this time, and for those of us in recovery, the emotional toll can become a trigger for unhealthy coping mechanisms. At Golden Gate Recovery, we understand how deeply personal grief is, and we’re here to support men navigating these challenges while maintaining sobriety.
Let’s explore how to manage holiday grief healthily, avoid self-medication, and honor your loved ones while preserving your well-being and sobriety.
Grief is a complex and deeply personal experience. During the holidays, emotions tied to loss can feel more intense because of the emphasis on family gatherings, traditions, and celebrations. For men in recovery, these heightened emotions can be particularly challenging to navigate.
Grief doesn’t have a timeline—it may hit hardest during the first holiday season without a loved one or resurface years later in unexpected ways. The key is recognizing that these feelings are valid and part of the healing process.

Certain aspects of the holidays can bring grief to the forefront, including:
Recognizing these triggers can help you prepare for and manage your emotions during the season.
If someone close to you is grieving during the holidays, here are ways to show your support:
For men in recovery, reaching out to peers who are also grieving can create a supportive space to share experiences and encourage sobriety.
Honoring the memory of someone we’ve lost can provide comfort and a sense of connection during the holidays. Reflecting on their life and the moments you shared helps keep their spirit alive in your heart. Here are meaningful ways to celebrate their memory:
Take time to reminisce about your loved one with family and friends. Share your favorite memories, funny anecdotes, or life lessons they taught you. Consider dedicating a moment during holiday gatherings for everyone to share their stories. This not only honors their legacy but also strengthens bonds among those who loved them.
Prepare a dish or dessert your loved one enjoyed, and include it as part of your holiday meal. Cooking their favorite recipe can bring back cherished memories and create a comforting sense of connection. You might even invite others to join you in the kitchen and share what this meal meant to your loved one.
Fill a box with photos, handwritten notes, or meaningful mementos that remind you of your loved one. This can become a cherished tradition during the holidays—opening the box each year to reflect on their life and the impact they had on you. Encourage others to contribute items or write down a memory to add to the collection.
Lighting a candle in your loved one’s honor can be a beautiful and calming ritual. Place the candles in a special spot and take a moment to reflect on the joy they brought to your life. You might also invite family members to gather around the candle to share a moment of silence or say a few words in their memory.
Consider donating to a cause or organization that is meaningful to your loved one. Whether it’s a local charity, a favorite nonprofit, or a cause related to their passions, this gesture can be a powerful way to honor their values and positively impact their memory.
Create a special display of your loved one’s photos as part of your holiday decorations. Whether it’s a single framed picture or a collage of favorite moments, seeing their smile can be a comforting reminder of their presence in your life. You could even include a short handwritten note about what they meant to you.
If your loved one had unique traditions or rituals they cherished during the holidays, consider continuing them. Whether it’s a specific way of decorating, a favorite song, or an annual activity, keeping these traditions alive can bring a sense of familiarity and warmth to the season.
Writing a heartfelt letter to your loved one can be a therapeutic way to express your feelings. Share your thoughts, recount your favorite memories, or let them know how much they’re missed. You can keep the letter in a special place, add it to a memory box, or even read it aloud during a private moment of reflection.
Design a personalized ornament to hang on your holiday tree in their honor. It could feature their name, a favorite quote, or symbols that remind you of them. Each year, placing this ornament on the tree can serve as a meaningful ritual that keeps their memory alive.
Your loved one’s legacy can live on through acts of kindness. Volunteering, helping a neighbor, or simply offering support to someone in need can be a powerful way to honor them. This can also create new, positive memories tied to their spirit of generosity or compassion.
While holding onto cherished traditions can be comforting, it’s also okay to adjust or create new ones. Some ideas include:
Creating new traditions doesn’t mean forgetting—it means finding a way to incorporate their memory into a healthier, forward-looking holiday experience.
One of the most important things to remember during the holidays is that you don’t have to navigate grief alone. Leaning on your support network is essential for emotional healing and maintaining sobriety.
The holidays are a time when connection can be a lifeline, especially for men in recovery who may otherwise feel isolated.

Permit yourself to feel. Suppressing grief can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms, including self-medication. Instead, embrace your emotions as a natural part of the healing process.
Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, can help ground you when emotions become overwhelming. Even a few minutes a day can provide clarity and peace.
You don’t have to meet every social obligation or create a perfect holiday. Focus on what feels meaningful and manageable for you.
Scrolling through idealized holiday posts can amplify feelings of sadness or comparison. Limiting screen time can help you stay present and focused on your journey.
The holidays can tempt us to numb our pain with substances, but this approach only compounds grief in the long run. Instead, rely on healthy outlets like exercise, journaling, or creative expression to process your emotions.
Anticipate potential challenges, such as attending events where alcohol is present. At Golden Gate Recovery, we encourage clients to have an “exit plan” for situations that might feel overwhelming or triggering.
Taking care of your physical health supports your emotional well-being. Ensure you’re eating well, staying hydrated, and getting enough rest.
Keep reminders of your recovery journey visible, whether it’s a sobriety token, a journal entry, or a letter to yourself. Let these serve as touchstones when grief feels heavy.

At Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, California, we understand how the holidays can bring a unique mix of joy and sorrow. For men in recovery, grief during this time can feel especially isolating, but it doesn’t have to derail your progress.
Our men’s rehab program offers a supportive environment where you can process grief, build resilience, and develop the tools to maintain sobriety. We believe that healing is a community effort, and we’re here to walk alongside you as you navigate the challenges of recovery.
This holiday season, let’s honor the memory of loved ones while embracing the possibilities of a sober, healthy future. If you’re struggling to cope or need additional support, reach out to Golden Gate Recovery today. Together, we can help you find strength, hope, and connection during the holidays and beyond.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:
Understanding the differences and connections between emotional and mental health is essential for overall well-being. Although these terms are often used interchangeably, they describe distinct aspects of our psychological and emotional states. Life is full of challenges—unexpected changes, overwhelming emotions, and stress can test even the strongest among us. The good news is that with the right tools, knowledge, and support, you can nurture both your emotional and mental health, even in tough times.
In this article, we’ll dive into what emotional vs mental health and where they overlap, and practical ways to care for both. Whether you’re facing life’s difficulties or simply looking to enhance your well-being, understanding these concepts is a powerful step toward a balanced and fulfilling life. After all, taking care of your mind and heart is the foundation for thriving, not just surviving.

Emotional health refers to your ability to manage your emotions, express them constructively, and cope with life’s challenges. It’s not just about feeling positive emotions like happiness or love but also acknowledging and processing negative emotions such as sadness, anger, or frustration.
When someone is emotionally healthy, they can:
Emotional health is closely tied to your relationships with others. It influences how you connect, empathize, and respond to those around you. In many ways, emotional health is the foundation for meaningful interactions and fulfilling personal relationships.
Mental health encompasses your cognitive, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how you think, perceive the world, and make decisions. Mental health is crucial at every stage of life, influencing your ability to cope with stress, work productively, and contribute to your community.
Good mental health includes:
Mental health can be affected by biological factors, such as brain chemistry, genetics, and physical health, as well as external influences like life experiences and social support.

Emotional and mental health are deeply intertwined. For example, when your mental health suffers due to stress or anxiety, your emotional health often takes a hit too, making it harder to manage your feelings. Conversely, unresolved emotional distress can affect your mental clarity and decision-making abilities.
Think of them as two sides of the same coin. While emotional health focuses on feelings and relationships, mental health is more about thoughts and cognitive functions. Both play a significant role in shaping your overall well-being. Focusing on one often results in positive changes in the other.
Although mental and emotional health are connected, they differ in several ways. Understanding these distinctions can help you identify areas needing attention and seek the right kind of support.
Psychological differences highlight how mental and emotional health affect distinct aspects of our internal experiences. Mental health relates to how the brain functions, focusing on cognitive processes such as memory, learning, and concentration. Emotional health, however, revolves around how emotions are processed and expressed, emphasizing feelings and interpersonal relationships more than purely cognitive functions.
Cognitive differences involve how thoughts and emotions are processed and managed. Mental health pertains to thoughts and perceptions, including challenges like distorted thinking patterns or chronic overthinking. On the other hand, emotional health focuses on understanding and regulating feelings, emphasizing the importance of recognizing emotions and maintaining a balanced emotional state.
Behavioral differences reveal how mental and emotional health issues can influence actions. Mental health struggles often lead to behaviors like withdrawing from social interactions, losing interest in hobbies, or neglecting responsibilities. Emotional health challenges, meanwhile, typically manifest as mood swings, irritability, or difficulty expressing emotions in healthy and constructive ways. These behavioral patterns can help identify the type of support or intervention needed.
Recognizing the signs of emotional and mental health struggles in yourself or others is key to providing support and seeking help. While they may overlap, certain triggers and symptoms can help distinguish between the two.
Caring for your mental and emotional health isn’t just about addressing problems when they arise; it’s about building resilience and maintaining balance through proactive habits. The following are the practical steps to enhance both your mental and emotional well-being:

Taking care of your emotional and mental health doesn’t have to be complicated—it’s about making small, meaningful changes that fit into your everyday life. Start with self-compassion. Think about how you’d comfort a close friend struggling, and offer yourself the same kindness. Life can feel overwhelming at times, and that’s okay. Let yourself feel what you’re going through without judgment, and remind yourself that tough days don’t last forever.
And if it feels like too much to handle alone, reaching out for professional help is a sign of strength, not weakness. At Golden Gate Recovery, you’ll find compassionate care tailored to your unique needs. Whether you’re dealing with anxiety, depression, emotional overwhelm, or mental health challenges stemming from life’s stressors, we offer a range of treatment options to help you regain balance, such as:
Remember, taking the first step toward support is a powerful act of self-care. At Golden Gate Recovery, we’re here to walk alongside you on your journey to healing and growth.
If you or someone you know is struggling with emotional or mental health challenges, Golden Gate Recovery is here to help. Our team of experts focuses on holistic healing, combining therapy, community support, and lifestyle changes to guide you toward recovery. Contact us today to start your journey!
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a complex neurological condition that affects many individuals, particularly men. The disorder manifests in various ways and can pose significant challenges in daily life. We’ll be exploring the intricacies of ADHD, particularly focusing on men, covering its symptoms, the unique challenges faced, the diagnosis process, and potential coping strategies.
If you or a loved one is struggling with ADHD and drug addiction, we’re here for you. At Golden Gate Recovery, we provide a bridge to recovery and a better life. Don’t hesitate to reach out for more information about our programs.
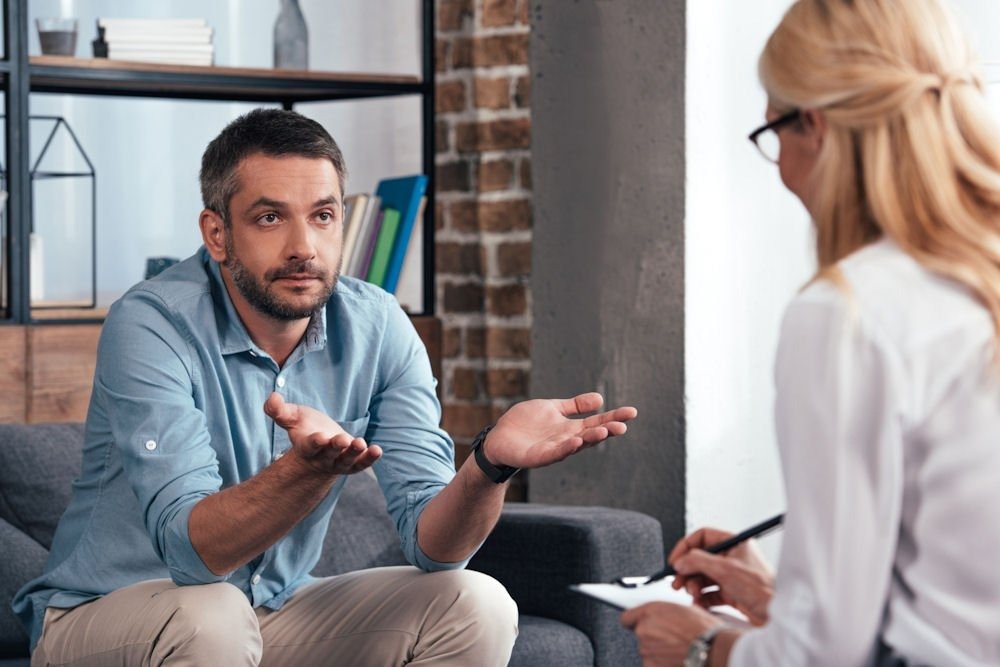

ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder usually identified in childhood but can continue into adulthood. It is characterized by difficulties in maintaining attention, hyperactivity, and impulsive behaviors. Understanding its core elements is vital in dispelling myths and recognizing its impact on those affected.
The symptoms of ADHD can manifest differently in various individuals, leading to a spectrum of experiences that can affect academic performance, social interactions, and emotional regulation. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for those with ADHD, enabling them to harness their unique strengths and navigate challenges more effectively.
ADHD stems from a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. Research shows that brain imaging studies reveal structural and functional differences in the brains of individuals with ADHD compared to those without. Specifically, areas responsible for impulse control, executive function, and attention appear to be less active.
These findings highlight the importance of understanding ADHD as a brain-based condition rather than a mere behavioral issue. Furthermore, studies have indicated that certain environmental factors, such as prenatal exposure to tobacco smoke or lead, may increase the risk of developing ADHD, suggesting that prevention strategies may play a role in mitigating its onset.
Neurotransmitters, particularly dopamine and norepinephrine, play a crucial role in attention and behavior. An imbalance in these chemicals may contribute to ADHD symptoms, leading to the challenges experienced in day-to-day activities. This biochemical perspective has led to the development of various treatment options, including stimulant medications that aim to restore balance in neurotransmitter levels. However, it's essential to recognize that medication is just one part of a comprehensive treatment plan, which may also include behavioral therapy, psychoeducation, and lifestyle modifications to support individuals in managing their symptoms more effectively.
Despite its prevalence, ADHD is often misunderstood. A common misconception is that ADHD is simply a result of poor parenting or laziness. This view undermines the complexities of the disorder, which is rooted in neurological differences rather than behavioral issues alone.
Such misconceptions can lead to stigma and feelings of shame for those affected, making it crucial to foster a more informed understanding of ADHD within society. Education and awareness initiatives can help shift public perception, promoting empathy and support for individuals navigating the challenges associated with ADHD.
Another misconception is that ADHD only affects children. While it is often diagnosed in childhood, many adults continue to experience symptoms, often unnoticed or untreated, leading to pervasive difficulties in various life domains. Adult ADHD can manifest in different ways, such as chronic disorganization, difficulty in maintaining relationships, and challenges in the workplace.
Recognizing that ADHD persists into adulthood is essential for developing appropriate support systems and resources tailored to adult needs, ensuring that individuals can thrive at every stage of life. Moreover, many adults with ADHD possess unique strengths, such as creativity and problem-solving skills, which can be harnessed positively in various professional and personal contexts.
Understanding the symptoms of ADHD in men is crucial for effective identification and management. While symptoms can manifest differently across genders, men may display certain traits more prominently. Recognizing these symptoms can facilitate timely intervention, which is essential for improving quality of life and fostering better relationships both personally and professionally.
Cognitive symptoms of ADHD can include difficulties in focusing, organizing tasks, and following through on projects. Men may find themselves easily distracted by external stimuli or struggle to prioritize effectively, which can hinder productivity both at work and in personal life. This can lead to a cycle of frustration, as tasks pile up and deadlines loom, creating an overwhelming sense of pressure.
Men with ADHD might also experience working memory deficits, making it challenging to recall information or manage time efficiently. These cognitive struggles can lead to frustrations in educational settings and the workplace, impacting overall performance. For instance, a man might forget important meetings or lose track of essential details in conversations, which can affect his reputation and relationships with colleagues. Furthermore, the inability to manage tasks effectively can lead to procrastination, further exacerbating stress and anxiety levels.
Emotional symptoms are often less recognized but are just as significant. Men with ADHD may experience mood swings, irritability, and increased sensitivity to stress. These emotional fluctuations can cause conflicts in personal relationships and affect mental well-being. The unpredictability of their emotional responses can leave partners and friends feeling confused or helpless, leading to strained connections.
Additionally, feelings of frustration, anxiety, and overwhelm are common. Men might find it hard to regulate their emotions, leading to impulsive reactions that can create further complications in social situations. For example, a sudden outburst during a disagreement can escalate tensions, making it difficult to resolve conflicts amicably. This emotional volatility can also contribute to a sense of isolation, as men may feel misunderstood or judged by those around them, further complicating their social interactions.
Behavioral symptoms of ADHD in men often include impulsivity, restlessness, and difficulty sitting still. This can manifest as fidgeting, interrupting others during conversations, or making hasty decisions without considering the consequences. Such behaviors can lead to a pattern of negative feedback from peers and authority figures, reinforcing feelings of inadequacy and frustration.
These behaviors can adversely affect relationships and professional interactions, as others may perceive them as disrespectful or inconsiderate. Recognizing these behaviors is essential for addressing them constructively. For instance, men may benefit from strategies that promote self-awareness and mindfulness, allowing them to pause and reflect before reacting. Engaging in activities that channel their energy, such as sports or creative pursuits, can also provide an outlet for their restlessness while fostering a sense of accomplishment and connection with others.
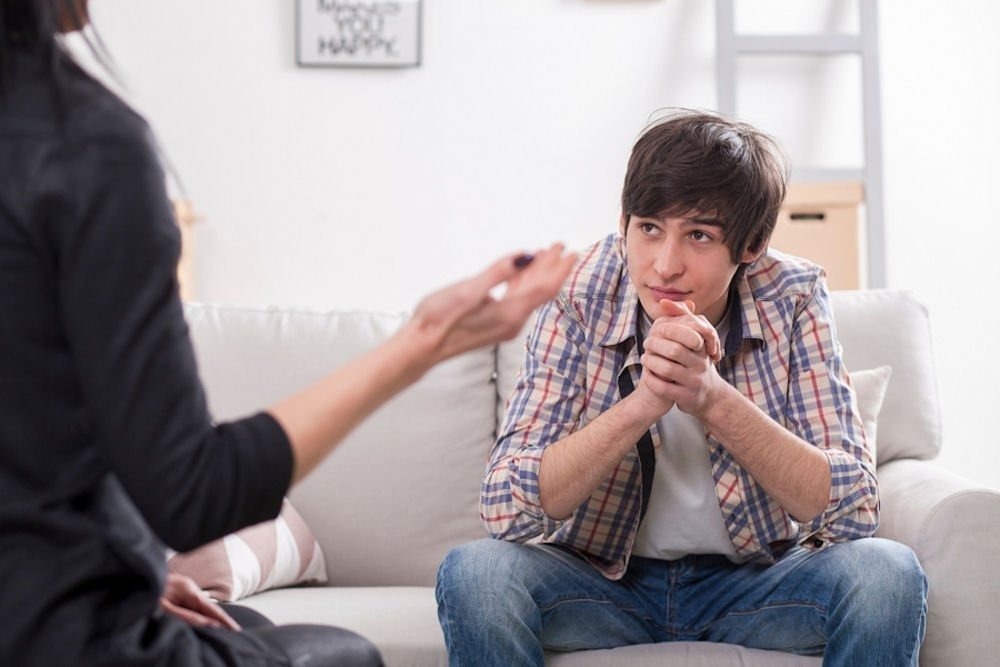

Men with ADHD often encounter challenges that can exacerbate their symptoms and impede their overall quality of life. Understanding these challenges is vital for developing effective coping methods.
Maintaining healthy relationships can be particularly challenging for men with ADHD. Their impulsive nature may lead to misunderstandings, while emotional symptoms can create barriers to effective communication.
Partners may struggle to comprehend how ADHD impacts behavior, leading to frustration and resentment. Moreover, men may feel isolated or misunderstood, creating a cycle that can further strain connections with others. This isolation can be compounded by a lack of awareness or understanding from friends and family, who may not recognize the nuances of ADHD. As a result, men with ADHD might withdraw from social situations, fearing judgment or misunderstanding, which can further exacerbate feelings of loneliness.
Men with ADHD may face distinct challenges in their professional lives, including difficulties in maintaining focus during meetings or completing tasks on time. The impulsive nature associated with ADHD can lead to sporadic work patterns and inconsistent performance.
These challenges may affect advancement opportunities and job satisfaction. Additionally, the stigma linked to ADHD can lead to underemployment or misinterpretation of a person’s capabilities. In workplaces that prioritize rigid structures and strict deadlines, men with ADHD may struggle to adapt, feeling overwhelmed or underappreciated. This can create a cycle of stress and anxiety that further hinders their ability to perform, leading to a potential decline in job performance and overall career fulfillment.
Fortunately, there are effective solutions and coping strategies available to help men manage ADHD. These strategies can significantly improve daily functioning and quality of life.
Medication is often a cornerstone in the treatment of ADHD. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, are frequently prescribed to help enhance focus and reduce impulsivity.
In addition to medication, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can be beneficial in addressing emotional symptoms and developing coping strategies, helping men better manage their condition.
Lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing ADHD symptoms. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and ensuring adequate sleep can improve overall brain function and mood regulation.
Incorporating mindfulness practices, such as meditation and yoga, may help men with ADHD develop better emotional control and reduce anxiety levels, providing additional avenues for coping.
Establishing a robust support system is essential for men with ADHD. Connecting with support groups, either in-person or online, can facilitate sharing experiences and strategies for managing symptoms.
Additionally, community resources, including mental health services and workshops, can provide valuable information and support networks, empowering men to take charge of their ADHD management.
Men struggling with ADHD may resort to drug or alcohol use to cope with their symptoms. This can be a destructive and problematic way of coping with the situation. In some cases, this coping strategy can lead to addiction which can create a cycle of continued drug use which makes the symptoms of ADHD worse. This can result in a co-occurring disorder, which is when a person deals with both a mental health disorder and an addiction.
In these cases, it’s important to get quality help that tackles both disorders uniquely but at the same time. Our professional and experienced team can help you tackle both facets with guidance and strength.
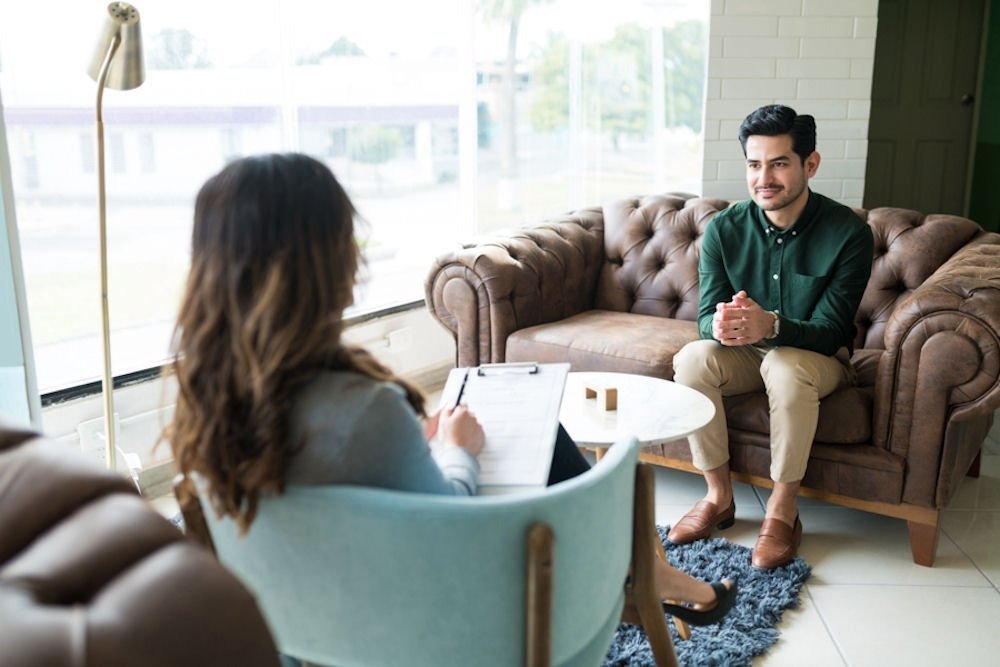

Along with several mental health treatment programs we provide dual diagnosis treatment for those struggling with both a mental health disorder and addiction. If you or a loved one is in this situation, look no further than Golden Gate Recovery. We are here to make sure your path to recovery is effective and smooth. Give us a call today to learn more about our programs.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for: