
When it comes to party nights or studying sessions, many people may turn to Adderall and alcohol to keep them going. Adderall, a prescription medication used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), helps boost focus and energy, while alcohol is often seen as a way to unwind and relax. But when mixed, these two substances can create a dangerous cocktail, leading to serious health risks that many don’t even realize. Despite their different effects on the body, the combination of Adderall and alcohol can cause unpredictable reactions, often putting your health and safety on the line.
In this article, we’ll explore why mixing Adderall and alcohol is so risky and what you need to know to stay safe. Let’s dive into the dangers and why it’s important to be aware of the potential consequences.
Adderall is a prescription medication commonly prescribed to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and narcolepsy. It contains a combination of two active ingredients: amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, both of which are stimulants that affect chemicals in the brain and nerves. Adderall helps increase attention, focus, and impulse control in individuals with ADHD.
However, it is also frequently misused, particularly by individuals looking to boost energy or alertness. This misuse, when combined with alcohol, can have serious consequences for both physical and mental health.

Both Adderall and alcohol come with a list of potential side effects, and when mixed, these effects can be amplified, leading to dangerous health risks.
When combined, these substances create an unpredictable mixture. Alcohol’s depressive effects counterbalance the stimulating effects of Adderall, potentially masking the feelings of intoxication, which leads people to drink more than they would otherwise. This can increase the risk of overdose or alcohol poisoning.
People may mix Adderall and alcohol for several reasons, but it is important to note that combining these substances is dangerous and can have serious consequences. Some reasons people might mix Adderall and alcohol include:
Adderall is a stimulant, while alcohol is a depressant. The stimulant effects of Adderall can make someone feel more alert and energetic, potentially masking the sedative effects of alcohol. This can lead people to drink more than they normally would because they don't feel as intoxicated as they actually are, increasing the risk of alcohol poisoning.
Some individuals may mix the two substances in an attempt to enhance the effects of one or the other. For instance, they might believe the stimulant effect of Adderall will counteract alcohol's depressant effect, making them feel "more in control" or "more energetic" while drinking.
Adderall may make some people feel more focused, talkative, or social. Some might combine it with alcohol in social settings to prolong their energy or prevent fatigue, especially during long nights out.
In some cases, individuals misuse Adderall or alcohol for recreational purposes. The combination may be used in an attempt to enhance feelings of euphoria or high energy.

Combining Adderall and alcohol is extremely dangerous due to the following reasons:
Adderall can mask the sedative effects of alcohol, making you feel less drunk than you actually are. This can lead to overconsumption of alcohol, significantly increasing the danger of alcohol poisoning, blackouts, and even death.
Adderall raises heart rate and blood pressure, while alcohol can cause dehydration. The combination can place significant strain on the heart, potentially leading to severe cardiovascular issues like heart attacks or strokes.
Adderall may initially enhance alertness, but alcohol impairs motor skills and decision-making. The combined effects reduce cognitive clarity, increasing the likelihood of accidents, risky behavior, and poor decision-making.
The combination of Adderall and alcohol can create a dangerous cycle of substance abuse. Adderall is frequently misused recreationally, and alcohol abuse is widespread. Together, they increase the likelihood of developing a substance use disorder and dependence.
Chronic use of both substances can severely impact mental well-being. Adderall can heighten anxiety and irritability, while alcohol worsens depression. This creates a vicious cycle where individuals use one substance to cope with the effects of the other, exacerbating mental health issues.
The risks associated with mixing alcohol and Adderall are severe and can include:
Both alcohol and Adderall place stress on the liver. Mixing the two can worsen liver damage over time, potentially leading to significant liver issues, including liver failure.
Both Adderall and alcohol are diuretics, causing dehydration. This imbalance can result in dizziness, muscle weakness, and even more severe issues, such as seizures, if not carefully managed.
Adderall can cause insomnia due to its stimulating nature, while alcohol may initially make you drowsy but disrupts your sleep cycle. The combination can lead to long-term sleep disturbances, resulting in fatigue, poor concentration, and a weakened immune system.
Adderall can initially enhance focus and alertness, but alcohol impairs cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and decision-making. When mixed, these effects can result in impaired cognitive performance, making it harder to concentrate and process information.
Both substances can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate temperature. Adderall can cause an increase in body temperature due to its stimulating effects, while alcohol impairs the body’s natural cooling mechanisms. This combination can significantly raise the risk of overheating, leading to heatstroke in extreme cases.

Withdrawal symptoms from either Adderall or alcohol can be severe, and when both substances are used regularly, withdrawal can be even more complicated. Symptoms may include:
In severe cases, withdrawal from either substance can result in seizures or death, particularly when not properly managed. Because Adderall and alcohol affect the body in different ways, attempting to quit both substances without professional help can be life-threatening.
Individuals seeking treatment for Adderall and alcohol addiction can access a variety of specialized programs designed to address both substance use disorders and any co-occurring mental health conditions. These programs typically integrate evidence-based therapies, medical supervision, and holistic approaches to support comprehensive recovery.
Inpatient programs create a supportive space where individuals can focus solely on their recovery, away from any outside distractions. These programs typically offer comprehensive treatment plans, including therapy, medical support, and family involvement.
Incorporating holistic therapies can complement traditional treatment methods. These approaches may include mindfulness, yoga, acupuncture, and other alternative therapies designed to support overall well-being.

Golden Gate Recovery is a leading rehabilitation center in California that specializes in helping individuals overcome polysubstance abuse, including Adderall and alcohol addiction. Our comprehensive treatment programs offer a combination of medical detox, individual and group therapy, and holistic services to support long-term recovery.
If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction, don’t wait to get help. Contact us today!
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Knowing how to spot the signs of alcohol poisoning is a crucial key to taking swift action. Here we reveal the signs of alcohol poisoning and how to respond. It takes swift and appropriate action to curb these serious conditions. Your actions in the moment could mean the difference between life and death. Heed the following vital information and connect with our superior treatment team to get someone the help they need today.
Alcohol poisoning is defined as a blood alcohol content of 30 percent or higher. These levels of intoxication are dangerously high levels that can send your body into shock, induce comas, or cause long-term health problems. This occurs because toxic alcohol levels in the body begin compromising vital organ functions to degrees beyond what the body is capable of processing. Immediately reach out to emergency services if you suspect you or a loved one may have alcohol poisoning.

Alcohol poisoning is not to be misinterpreted as simply being drunk. They are two different levels with separate sets of symptoms and signs. Alcohol poisoning is a much higher level of intoxication acquired by consuming large quantities in a short amount of time. This degree of consumption comes with dangerous and potentially fatal consequences. Drunkenness or intoxication, on the other hand, is an altered state of mind that is a bodily reaction to the absorption and metabolization of alcohol. Only when your body has reached its capacity of being able to metabolize does it begin to border on alcohol poisoning.
Alcohol poisoning is easy to spot if you know the behavioral indicators. Even mental signs of alcohol poisoning give off behavioral and physical cues. Here are some of the most common signs and how they manifest themselves.
A drunk individual will have some form of staggered walk. However, an individual with alcohol poisoning will have severely exacerbated manifestations of this symptom. This will portray itself in excessive staggering to the point of being rendered incapable of walking without inducing serious self-harm. This means frequent falling, “jelly leg” like instability, or other similar observable movement deficiencies. Under such circumstances, the individual will need help simply to walk and should not do so alone.
When you're drunk, it's common to slur your words. However, alcohol poisoning takes this to the extreme by causing severely slurred speech. In many cases, people who are exhibiting signs of an impending alcohol poisoning overdose will have indiscernible speech. This is no laughing matter and should be taken seriously. Reach out to local emergency services if someone develops indiscernible speech slurring in conjunction with a drinking session.
When your mind and body have reached their limit, it will begin to shut down or go into a comatose state. This occurs because the body goes into a full shutdown in an attempt to repair and cleanse the body of alcohol toxins. This sign of alcohol poisoning will exhibit itself as nodding in and out of consciousness. This means literally “nodding off” and momentarily reawakening intermittently. In some cases, it can be slept off, but this symptom should be met with swift medical assistance to ensure their safety.
Nausea and vomiting are signs of binge drinking or overconsumption of alcohol. What’s worse is that vomiting further dehydrates your body, increasing your susceptibility to poisoning. It’s important to keep an eye on such instances, as this can be a serious sign of alcohol poisoning. This can lead to alcohol toxin-related blackouts that require immediate medical attention. Seek out the appropriate professionals if you or a loved one begins exhibiting this symptom.
Excessive alcohol consumption or intoxication that borders on poisoning will have severe effects on one’s psyche. This means potential memory lapses, mind fog, or complete obliviousness to one’s surroundings. This can also render the poisoned individual incapable of carrying on a conversation or responding appropriately to simple social communications. These intoxication levels not only pose over-intoxication dangers, but also potential self-harm stemming from distorted or confused circumstances.
An alcoholic blackout is a situation where an individual drinks so excessively that it induces memory loss. These memory lapses can range from mild to severe and be temporary or permanent, depending on the severity. This means they’ll wake up with no recollection of the events leading up to, during, or after their drinking. Indications of a blackout reveal themselves through severe disorientation, coordination, and cognitive ineptitude, and other circumstantial disorientations.
One of the obvious tell-tale indicators of alcohol poisoning involves life-threatening seizures. This is the most severe phase of alcohol poisoning that needs immediate medical help. This occurs when alcohol poisoning is so severe that it sends your body into shock and convulsive. This can be the result of overconsumption, allergic reactions, or other negative bodily reactions that trigger this extreme response.
Incontinence is a term that describes one’s inability to control bladder or bowel movements. If you or a loved one exhibits this sign, it’s a very dangerous sign that your body is in fight-or-flight mode as a result of alcohol poisoning. That's because all organ functions and control are released when your body is trying to fend off near-fatal levels of intoxication.
Slow breathing and respiratory distress are very common adverse bodily reactions to alcohol poisoning. Slow breathing is characterized by fewer than eight breaths within 60 seconds. Correlatively, respiratory distress is defined as oxygen levels that fall below 94 percent. If you or someone you love is experiencing difficulty breathing in conjunction with a drinking session, don't ignore this serious sign of overconsumption of alcohol.

Seeking addiction rehab at Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, California, is the best way to steer clear of alcohol-related incidents. Here are a few of the many ways treatment helps you prevent harmful incidents from recurring.
Alcohol rehab is all about learning and implementing relapse prevention techniques. These methods are intended to be exercised if overwhelming cravings arise. These also help you react proactively to any hardships that may arise that could tempt you into relapse. The best aspect of these techniques is that they are independently implementable once ingrained into your natural impulsive responses.
Nothing helps you fend off dangerous alcohol sessions and incidents like having a strong accountability structure. That's exactly what Golden Gate Recovery strives to maximize in all of our recovery programs: total support and maximum accountability. Therefore, anytime discouragement or relapse urges arise, you have the full-spectrum support you need to overcome these difficult times.
The greatest way to prevent drinking-induced incidents is to avoid environments and bonds that encourage these drinking habits. Alcohol therapy treatment achieves this by surrounding you with sober-friendly influences and circumstances. Hence, these new exposures to sober individuals help form the new sober friendships needed to help you shape the positive influences that keep you accountable.
The most effective incident prevention methods involve the healthy habits you form in recovery treatment. Our highly effective treatment techniques target the foundational routines of your alcoholic tendencies and remove them at the source. Once removed, we implement new habits based on your joys, desires, and newly discovered enjoyable hobbies. That way, your newly-formed habits aren't of our doing. They're routines you have a passion and a desire to indulge in eagerly every day to proactively replace those former tendencies.
Most individuals who abuse alcohol do so because their dependency requires them to indulge just to keep torturous withdrawals at bay. This alone leads to serious alcohol-related hardships and incidents. Therefore, detox programs provide that vital cleansing needed to conquer your strongholds once and for all. You'll find total liberation and a clear path to sobriety by enrolling in our life-changing detox programs.
Anybody showing evident signs of alcohol poisoning needs immediate medical help. Bearing that in mind, here is how to respond upon observing any of the aforementioned symptoms:

You need alcohol addiction treatment if you have experienced or come near experiencing any of the aforementioned dangerous signs and symptoms. Furthermore, if you’ve exhibited any withdrawal symptoms or the inability to refrain from drinking, the next step for you is to enroll in alcohol addiction rehab.
Contact Golden Gate Recovery in California to embark on your burden-alleviating recovery journey. We’re here to help you conquer the most difficult rehab hurdles and accomplish true remission from your alcoholic strongholds. Step through the doors of Golden Gate Recovery today to begin the first day of a healthier life.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Alcohol is primarily a depressant, slowing brain function and impairing coordination. However, in small amounts, it can have stimulating effects, increasing heart rate and social behavior. As consumption rises, its depressant effects dominate, leading to sedation and impaired judgment. Understanding alcohol’s impact helps with responsible consumption and health awareness. Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, California, is an alcohol rehab for men, providing detox, therapy, and support to achieve lasting sobriety in a safe, structured environment.
Alcohol is a psychoactive substance that alters brain function, affecting mood, cognition, and behavior. It is commonly found in beverages like beer, wine, and spirits, produced through fermentation or distillation. Classified as a depressant, alcohol slows the central nervous system, impairing motor skills and judgment. However, small doses may create stimulating effects, increasing sociability and reducing inhibitions.
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to dependence, addiction, and serious health risks, including liver disease, heart problems, and cognitive decline. Understanding its effects is crucial for responsible use and overall well-being.
Alcohol affects the brain by slowing neurotransmitter activity, leading to impaired judgment, coordination, and memory. It disrupts communication between nerve cells, reducing cognitive function and emotional regulation. Initially, alcohol may create a feeling of relaxation or euphoria, but as consumption increases, its depressant effects take over, causing drowsiness and slowed reflexes.
In the body, alcohol impacts vital organs like the liver, heart, and digestive system. It can lead to dehydration, increased blood pressure, and long-term risks such as liver disease and weakened immune function. Responsible consumption is crucial for overall health.
Alcohol is not a true stimulant, though it can produce stimulating effects at lower doses. Initially, it may increase heart rate, elevate mood, and enhance sociability by affecting neurotransmitters like dopamine. This can create a temporary sense of energy and excitement, often mistaken for stimulation. However, these effects are short-lived.
As consumption continues, alcohol’s depressant properties dominate, slowing brain function, impairing coordination, and reducing reaction time. It suppresses the central nervous system, leading to sedation and decreased cognitive function. Understanding these effects is key to responsible alcohol use.
Alcohol is not a stimulant because it primarily slows down the central nervous system. While small amounts can initially increase heart rate and sociability, these effects are short-lived and misleading. Unlike true stimulants, which enhance alertness and energy, alcohol disrupts neurotransmitter activity, impairing cognitive function and motor skills.
As consumption increases, alcohol’s depressant properties dominate, leading to sedation, slower reaction times, and reduced coordination. It suppresses brain function rather than enhancing it, distinguishing it from substances like caffeine or amphetamines, which actively stimulate neural activity.
Alcohol exhibits a biphasic response, meaning its effects change depending on the amount consumed. Initially, at lower doses, alcohol can act like a stimulant by increasing heart rate, boosting dopamine levels, and enhancing sociability. This phase creates a temporary sense of energy, relaxation, and reduced inhibitions, leading many to associate alcohol with stimulation.
However, as consumption continues, alcohol’s depressant effects become dominant. It slows brain activity, impairs coordination, and reduces reaction time. This sedative phase leads to drowsiness, cognitive impairment, and suppressed nervous system function, reinforcing alcohol’s classification as a depressant.

Stimulants and depressants affect the central nervous system in opposite ways. Stimulants, like caffeine and amphetamines, increase brain activity, elevate mood, and boost energy by enhancing neurotransmitter function. They promote alertness, improve focus, and often raise heart rate and blood pressure. These substances are commonly used to enhance cognitive performance or combat fatigue.
Depressants, including alcohol and benzodiazepines, slow brain function, reduce anxiety, and produce sedative effects by decreasing neurotransmitter activity. They impair coordination and cognitive processing, leading to relaxation or drowsiness. Overuse can result in dependence and serious health risks.
Alcohol can exhibit stimulant-like effects in low doses by increasing dopamine levels and boosting sociability. Initially, it may enhance mood, energy, and confidence while slightly raising heart rate. These effects can make alcohol feel invigorating, but they are short-lived.
Despite this temporary stimulation, alcohol is primarily a depressant. As consumption continues, it slows brain function, impairs coordination, and reduces reaction time. This shift highlights alcohol’s true nature, emphasizing the need for responsible use.
At low doses, alcohol can produce stimulant-like effects by increasing dopamine levels, elevating mood, and enhancing sociability. It may also lead to heightened energy, reduced inhibitions, and increased heart rate, creating a temporary sense of alertness and confidence. These effects, however, are short-lived and give way to alcohol’s depressant properties as consumption continues.

Alcohol is a depressant that slows brain function and impairs coordination by increasing GABA activity, leading to relaxation and sedation. Initially, it may lower anxiety and create a sense of calm, but as consumption continues, it diminishes cognitive abilities and motor skills.
At higher doses, alcohol suppresses the central nervous system, causing drowsiness, slowed reaction time, and impaired judgment. Long-term use increases the risks of dependence, memory issues, and serious health complications like liver disease and depression.
Alcohol slows brain function, impairing judgment, coordination, and reaction time. It enhances the activity of GABA, a neurotransmitter that induces relaxation and drowsiness. As consumption increases, alcohol suppresses the central nervous system, leading to sedation and cognitive impairment. Long-term effects can include dependence, memory issues, and serious health risks such as liver damage and cardiovascular problems. Understanding these depressant effects is crucial for responsible consumption and overall well-being.
Alcohol’s depressant effects become dangerous when coordination, reaction time, and cognitive function are severely impaired. Warning signs include slurred speech, confusion, excessive drowsiness, or difficulty staying awake. In extreme cases, alcohol poisoning or respiratory depression can occur, requiring urgent medical attention.
Long-term heavy drinking increases the risk of dependence, memory loss, and mood disorders. Identifying these effects early can prevent harm and support healthier choices, ensuring responsible consumption and overall well-being.
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is a chronic condition characterized by an inability to control alcohol consumption despite negative consequences. It affects brain chemistry, leading to cravings, tolerance, and dependence. Symptoms range from excessive drinking to withdrawal when not consuming alcohol. Long-term effects include liver disease, cognitive decline, and increased mental health risks. Early intervention, addiction counseling, and medical support are crucial for recovery.
Treatment for alcohol addiction involves medical and therapeutic approaches tailored to individual needs. Detoxification is often the first step, helping individuals safely withdraw from alcohol while managing withdrawal symptoms. Medication-assisted treatment (MAT), such as naltrexone or acamprosate, can reduce cravings and support recovery. Therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and group counseling, helps individuals develop coping strategies and address underlying issues.
Long-term recovery includes support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and outpatient or residential rehab programs. Other treatments that can further enhance healing and relapse prevention are holistic approaches, such as mindfulness and exercise.
Alcohol initially boosts dopamine levels, creating feelings of euphoria and relaxation. This temporary high can enhance social interactions and mask underlying stress or anxiety. However, as alcohol’s effects deepen, it disrupts neurotransmitter balance, leading to mood instability and emotional distress.
Long-term use can worsen mental health, increasing risks of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. Dependence may develop, creating a cycle where alcohol is used to cope but ultimately intensifies despair. Responsible consumption is essential for mental well-being.
Excessive alcohol use can contribute to mental illness by disrupting brain chemistry, worsening symptoms of depression and anxiety, and increasing the risk of alcohol-induced disorders. Dependence and prolonged use can lead to cognitive decline and emotional instability, making professional treatment essential.

Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, CA, offers specialized alcohol rehab for men, providing personalized treatment to support long-term recovery. Our evidence-based addiction treatment programs include detox, therapy, and peer support, addressing addiction and its underlying causes in a structured, healing environment.
With a focus on men’s unique challenges, we create a safe space for rebuilding lives through professional care and guidance. Our dedicated team helps individuals regain control, achieve sobriety, and develop strategies for lasting wellness. Begin your recovery journey with us by contacting us today.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Many people wonder about the safety of combining Tylenol and alcohol. Tylenol, whose active ingredient is acetaminophen, is one of the most commonly used over-the-counter pain relievers and fever reducers worldwide. Alcohol, conversely, is commonly used in social and recreational settings. However, mixing these two substances can be dangerous, primarily due to how they affect the liver.
This article explores how Tylenol and alcohol interact, who may be more at risk, and the precautions you should take when using Tylenol around the time of alcohol consumption. We will also discuss how long Tylenol lasts in the body and provide resources for those who may need help with polysubstance abuse or are searching for rehab for alcohol in California and other substance use disorders.
If you or a loved one is struggling with substance abuse, Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, California, offers expert support and personalized treatment to help you safely recover and regain control of your life.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and alcohol are both processed by the liver through enzymatic pathways. When taken separately at recommended doses, each is generally safe. However, when combined—especially in large amounts—they can interfere with each other’s metabolism and increase the risk of liver injury.
Tylenol is metabolized into mostly harmless substances, but a small fraction is converted into a toxic compound called N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI). Under normal conditions, the liver neutralizes NAPQI using glutathione, a natural antioxidant. Excessive acetaminophen intake or depleted glutathione levels allow NAPQI to build up, which damages liver cells. Alcohol affects this process differently depending on the pattern of consumption.
Regular heavy alcohol use reduces glutathione reserves and impairs liver function. This makes it harder for the liver to detoxify NAPQI, increasing vulnerability to acetaminophen toxicity even at normal doses.
Drinking alcohol shortly before or after taking acetaminophen activates liver enzymes like cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1). This enzyme converts more acetaminophen into the toxic NAPQI, raising the risk of immediate liver damage.
Understanding these interactions is crucial for minimizing the risk of liver injury when using acetaminophen in the context of alcohol consumption.
Acetaminophen alone can cause toxic liver damage called acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. This toxicity is the most common cause of acute liver failure in the United States, resulting in an estimated 56,000 hospital visits each year.
Acetaminophen is metabolized in two ways. First, about 90% of the drug is processed by the body through a process called glucuronidation, which does not produce dangerous byproducts. Second, the liver enzyme CYP2E1 breaks down about 5-10% of the drug, resulting in the formation of a toxin known as NAPQI.
In response, the liver produces an antioxidant called glutathione, which the body uses to remove the toxin before it can build up and damage the liver. When alcohol enters the body, it increases the activity of CYP2E1, which leads to increased production of the toxin NAPQI. Alcohol also reduces glutathione production, which means NAPQI is more likely to accumulate in the liver at dangerous concentrations.

The liver plays a central role in breaking down both acetaminophen and alcohol, helping to detoxify the body. Acetaminophen is mostly converted safely, but its toxic metabolite NAPQI must be quickly neutralized by glutathione to prevent harm.
Alcohol is primarily metabolized by enzymes such as alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and CYP2E1. Chronic or heavy alcohol consumption increases CYP2E1 activity, which in turn elevates NAPQI formation from acetaminophen metabolism.
Over time, repeated exposure to alcohol and acetaminophen can lead to oxidative stress and inflammation within the liver. This can cause a range of liver conditions, including:
As liver damage progresses, its ability to process drugs and alcohol diminishes, creating a cycle of increasing vulnerability. This highlights why combining acetaminophen and alcohol, especially frequently or in high amounts, can accelerate liver injury and related diseases such as cirrhosis, which can be deadly.
Acetaminophen overdose can cause acute liver damage, liver failure, and even death in the most severe cases. Here are the signs that you may be an alcoholic. It’s important to recognize these symptoms of liver damage, which include:
Because these symptoms may take several days to appear, it is important to monitor your health closely and seek medical attention promptly if any occur.
Not everyone faces the same level of risk when mixing acetaminophen and alcohol. Several factors can increase susceptibility to liver damage:
If you belong to any of these groups, it’s particularly important to avoid taking acetaminophen and alcohol together and to consult a healthcare professional before using pain relievers.
Many people often ask if it’s safe to take Tylenol after drinking alcohol. The answer varies based on factors like the amount of alcohol consumed, liver health, and timing:
Understanding how long Tylenol and alcohol stay in your body is helpful to manage the withdrawal timeline. After taking a typical dose of acetaminophen:
Because Tylenol and alcohol both strain the liver, spacing out their consumption to allow the liver to process each substance effectively is important.
Understanding the risks of mixing Tylenol and alcohol is important, but knowing how to reduce those risks is even more vital. Here are practical steps you can take to protect your liver and safely manage pain or fever relief:
Never take acetaminophen while actively drinking. Allow several hours after drinking before taking Tylenol so your liver can properly metabolize the alcohol.
Stick to label or doctor instructions. Do not exceed the maximum daily dose (usually 3,000–4,000 mg) to protect your liver.
Cut down on alcohol, especially if you regularly use acetaminophen. Reducing alcohol intake eases the burden on your liver and lowers the risk of damage.
If you have liver disease or a history of liver problems, talk to your healthcare provider before taking acetaminophen or drinking alcohol. They can advise you on safer alternatives and monitor your liver health.
Watch for symptoms like yellow skin, dark urine, nausea, or fatigue after acetaminophen or alcohol use; seek medical help immediately.
If you plan to drink or have a history of alcohol abuse or prescription drug abuse in your family, it’s important to discuss alternative treatment options with your doctor.
Abusing acetaminophen (Tylenol), especially with alcohol, can cause serious health issues like liver damage. Recovery usually needs professional help through various effective treatment programs for alcohol addiction.

If you or a loved one is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, help is available. Golden Gate Recovery in California offers compassionate, professional treatment programs designed to support your journey to lasting recovery. Contact us to learn more about their services and how they can help you regain control. Your path to healing starts here!
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

When alcohol enters your body, it triggers a metabolic process. Metabolism refers to the body’s chemical mechanism for breaking down substances so they can be absorbed or used for energy. This process happens whenever you consume food or beverages.
The liver primarily metabolizes alcohol. Typically, an individual can process about one alcoholic beverage per hour; however, this rate may vary based on factors such as weight, height, gender, and overall body composition.
Continue reading to discover how long alcohol stays in your system, including its presence in different bodily fluids such as blood, urine, saliva, and hair.
The duration for which alcohol remains detectable in your system can differ based on the quantity consumed, the type of testing method employed, and individual physiological characteristics.
Alcohol detection methods can identify its presence in your body for up to 6 hours following your last drink. Breath, saliva, and urine tests can reveal alcohol consumption for 12 to 24 hours after use, while hair follicles can retain traces of alcohol for as long as 90 days. The question is, how long does alcohol stay in your system?
Alcohol’s lifespan in the body ranges from as little as 6 hours to as much as three days. System duration depends on variables such as the amount consumed, drinking history, and level of dependency. In some cases, alcohol’s lifespan in the body can even exceed three days in the most severe cases. Bear in mind that these numbers merely reflect the initial cleansing of alcohol use and not the detox process duration.
Alcohol has a profound negative impact on brain functions as well as other vital organs. Here is a scientifically detailed overview of alcohol’s mental and physical effects.
Alcohol not only soaks up all the water in your body. It also soaks up a considerable amount of brain resources. Since alcohol is a known diuretic, it rapidly seeps precious bodily resources from your body. In the same regard, alcohol’s short-term brain effects on impaired cognitive functions, memory, and balance are perfect examples of brain dehydration. The more dehydrated you are, the worse these impairments will be.
Alcohol is considered toxic to your mind and body. Therefore, when alcohol reaches the brain, its high toxicity levels can incur permanent brain cell damage. The more deprived your mind and body are of water, the more deprived they are of necessary oxygen nutrients. Consequently, the long-term effects of exposing the brain to prolonged alcoholic toxicity can eventually lead to stroke and permanent brain defects.
Alcohol’s depressive effects on the central nervous system trickle down into slowing your digestive and metabolic processes. This is because vital organs like the liver and kidneys are forced to work overtime to process and expel alcohol and its toxic compounds from your body. Another reason digestion is slowed is due to alcohol’s relaxant effects on stomach muscles that play a key role in normal digestive functions.
The presence of alcohol in your system slows and weakens your immune system response. Therefore, if you drink in conjunction with being sick, it will take your body longer to fight off infections or other illnesses. In addition, it makes your body more prone to contracting additional infections or diseases. This is especially more pronounced in individuals who are heavy drinkers. This persistent weakening of the immune system can make you susceptible to increased carcinogen exposure linked to several cancers.
This is a long-term version of prolonged brain cell toxicity. While alcohol can damage brain cells in the short term, continued cell damage will eventually lead to permanent consequences. That means permanent brain damage when enough cells have been harmed. Thankfully, you can stop or prevent these mental harms by seeking immediate consultation from our empathetic care team

Quitting alcohol isn’t so easy because several environmental, mental, and experience-based causes drive people to drink. That’s why people who want to stop feel incapable of doing so for one or more of the following reasons.
Going through traumas like physical or mental abuse, military service, near-death experiences, or other traumas commonly drives people to drink. As with the others on this list, alcohol is always a way to cope or escape these underlying traumas or causes. This means you may have undiagnosed PTSD in conjunction with a drinking problem.
Depression is one of the top causes of substance and alcohol misuse and abuse. Depression and drinking are a dangerous combo for several reasons. For starters, these bouts of sadness induce self-destructive addiction and alcohol abuse cycles, without any care or regard for oneself. Secondly, drinking exacerbates depressive thoughts that could lead to rash, poor decision-making with potentially fatal outcomes. Treating your pre-existing depression disorders through dual-diagnosis treatment can, in turn, help you with your acquired drinking habit.
Alcohol’s depressive effects on the body are especially enticing to individuals with elevated anxiety levels. For people with naturally high anxiety or anxiety disorders, alcohol can feel as if it provides stress alleviation. However, studies find that though alcohol’s initial effects may lower anxiety, it boosts anxiety and stress levels after the fact. This includes exacerbating pre-existing anxiety disorders.
Having a pre-existing substance abuse problem increases the likelihood of developing alcohol dependence. This stems from an underlying dependency producing an unquenchable urge for a better high. This leads to attempting to mix the two for exacerbated effects. This is both an increased risk and danger since drugs and alcohol are a potentially lethal mix.

Addiction doesn’t come without very evident mental, physical, and behavioral cues. Seek immediate therapeutic help if you exhibit any of the following addiction signs.
People with an addiction are incapable of drinking responsibly. Hence, they’ll often drink beyond their limits, rendering them cognitively and mentally impotent, potentially to the point of blacking out. Drinking above your limits further means greater susceptibility to alcohol poisoning. If you or a loved one displays the inability to contain or limit their drinking habits, seek help now.
If you wish to know the extent of your addiction, look at your bank account. If a considerable amount of your finances goes towards purchasing alcohol, finances tell the full story of where one’s addiction lies. These financial tolls seep into affecting other financial obligations like rent, utilities, or other more important bills. We understand the stressful impacts of addiction-induced financial strains. That’s why Golden Gate Recovery is devoted to working with approved insurance plans to help lower the cost of the care you need.
Alcohol addiction takes a toll on your daily life, especially your work performance. People who frequently drink the night before often wake up late, resulting in recurring issues with punctuality. Furthermore, your energy levels and mental alertness needed to perform job functions will suffer due to alcohol’s after-effects.
Being dishonest to any degree about one’s drinking habits is an inherent indication that the person knows there’s a problem. This can include self-denial, dishonesty with themselves about their habits, or lying to others about the extent of their drinking. This is telling of more than just an addiction problem. These denial behaviors are a serious problem if the person is incapable of coming to terms with the nature of their struggles.
People with an alcohol addiction will harbor irresistible cravings. Regardless of one’s intentions, one will be incapable of resisting their drinking habit at some point. This is where our medical detox programs, administered under strict doctoral guidance, come into play. We’ll help you overcome these cravings through meticulous withdrawal symptom management techniques as your body cleanses itself of alcohol toxins.
Alcoholic shakes are uncomfortable tremors you experience when your body and mind are craving another drink. These shakes usually occur after the effects of an excessive drinking session begin to taper, onsetting within a few hours of your most recent drink. If you’re experiencing symptoms of alcohol-induced shakes, it’s imperative to contact a detox specialist immediately.
Alcohol dependency manifests itself through elevated anxiety, the longer you go without drinking. For people addicted to alcohol, these stress levels will become increasingly intolerable until a drink calms their nerves. You don’t have to suffer through these alcohol-induced anxiety withdrawals thanks to our revolutionary treatment approach. We’ll minimize your anxiety-based withdrawal symptoms and relieve the stresses associated with alcohol addiction.
Experiencing frequent headaches after the effects of drinking wear off is more than just a hangover. It’s a deeper symptom of a serious alcohol dependency. These headaches range from mild to extreme, depending on the severity of your addiction, among other personalized factors. Alcoholic headaches and migraines alone are enough to send anybody into an alcohol relapse. You can have peace of mind knowing you don’t have to suffer the full extent of these uncomfortable withdrawals.

The most important question isn’t, How long does alcohol stay in your system? It’s “How long will you allow alcohol to keep you from recovery?” We can help you bring permanent closure to the latter question simply by contacting Golden Gate Recovery today. Doing so will lift the burden of addiction that has been hindering a happier and sober you from breaking free. Break free from the bonds that have been holding you hostage to your drinking habits. Reach out to us to free yourself from the clutches of alcohol today.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Ulcers and alcohol often go hand in hand, but how exactly are they connected? Ulcers, which are painful sores that form in the lining of your stomach or small intestine, can make everyday life feel uncomfortable, even more so when paired with alcohol. Whether you’re a casual drinker or someone who enjoys a nightly glass of wine, it’s important to understand the connection between alcohol and ulcers to protect your digestive health.
Alcohol can disrupt the balance of your stomach’s protective barriers, increasing stomach acid and reducing mucus production, two key factors that contribute to ulcer formation. This combination can lead to inflammation and irritation, creating the perfect environment for developing ulcers.
If you’ve noticed stomach pain, nausea, or bloating after drinking, it might be worth exploring how alcohol could impact your digestive health. Understanding this connection can help you make informed choices about your alcohol consumption and prevent discomfort down the line. Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, California can help you or a loved one recover.
Excessive drinking is when you’re knocking back more alcohol than is considered safe or responsible. For most adults, binge drinking means having 5 or more drinks in a short period for men, or 4 for women. If you’re drinking frequently at this level or more, it’s considered excessive. But even if you’re not going that far, heavy drinking (defined as having more than 8 drinks per week for women or 15 for men) can still have negative effects on your health.
Drinking too much alcohol can mess with your stomach, with one of the potential issues being ulcers. Your stomach produces acid to help digest food, but when you overdo it with alcohol, that acid can irritate the stomach lining, making it more likely to develop ulcers. Heavy drinking can also weaken your body’s ability to heal from the damage caused by acid. So, if you’re noticing stomach pain, bloating, or discomfort, it might be worth keeping an eye on your alcohol intake. Too much of anything can take a toll on your body!
An alcoholic ulcer isn’t a specific type of ulcer, but it’s a term often used to describe the kind of ulcers that can form from drinking too much alcohol. When you drink a lot, the alcohol can irritate the lining of your stomach, leading to sores or ulcers. These ulcers can cause symptoms like stomach pain, nausea, and discomfort. Heavy alcohol consumption messes with the protective layer of your stomach, making it more vulnerable to stomach acid.
If you’ve got an alcoholic ulcer, chances are you’ll feel some pretty uncomfortable stomach symptoms. It might feel like a dull, gnawing pain in your stomach that doesn’t go away easily. Some people describe it as a sharp or burning sensation, especially after eating or drinking things like alcohol or spicy foods. You might also feel bloated, nauseous, or even throw up. The pain can worsen when your stomach is empty, and sometimes it might even wake you up at night. If you’re experiencing these kinds of symptoms, it’s a sign something’s not right, and it might be time to cut back on the drinking and talk to a doctor.
If you’ve got an ulcer caused by drinking too much alcohol, there are some signs and symptoms to watch out for.
A dull, burning, or sharp pain, especially in the upper abdomen.
Feeling full, bloated, or nauseous after eating or drinking.
A burning sensation in the chest, especially after consuming alcohol.
Discomfort, gas, or a feeling of fullness after meals.
Discomfort makes you not want to risk eating anything.
Pain or discomfort that worsens at night, making sleeping difficult.
Occasional or persistent vomiting, especially when drinking alcohol.
Feeling tired or weak, which can be linked to digestive issues.
Alcoholic ulcers don’t just pop up out of nowhere – they’re caused by a mix of factors that mess with your stomach lining.
Drinking alcohol when you have a stomach ulcer is like throwing gasoline on a fire—it makes everything worse.
Drinking alcohol can make your stomach pain, nausea, and bloating much worse.
Alcohol slows down your body’s ability to heal ulcers, meaning they can stick around longer.
Alcohol raises stomach acid levels, making the ulcer even more irritated and painful.
Drinking while you have an ulcer can lead to bleeding, infection, or more serious stomach issues.
Continued drinking can cause more discomfort, making it harder to eat and maintain a healthy diet.
Over time, the combination of alcohol and ulcers can lead to more severe digestive problems or other complications.

You can, but that wouldn’t be the smartest option. It’s generally not recommended to drink alcohol if you have a stomach ulcer. If you do decide to drink, it’s best to limit your alcohol intake as much as possible. Stick to smaller amounts of low-alcohol drinks, and avoid things like beer, whiskey, or mixed drinks that are high in acidity or sugar, as they can be particularly tough on your stomach. It’s always a good idea to check with a doctor before making any decisions about alcohol consumption, especially when dealing with ulcers.
If you’re worried you might have a stomach ulcer, here’s what you can do:
You can still have a lot of fun while drinking a lot less. Here are ways you can limit yourself to protect your health.
Decide how much you want to drink and stick to it.
Keep a journal or use an app to monitor how much you’re drinking.
Try non-alcoholic drinks like sparkling water or mocktails.
Keep yourself occupied with hobbies or activities that don’t involve alcohol.
Don’t chug it, take your time and savor the flavor.
Surround yourself with friends who support your decision to cut back.
Pay attention to how alcohol makes you feel—then decide if it’s worth it.
Focus on what you’re trying to achieve by reducing your drinking.
Celebrate small wins and treat yourself when you meet your goals.
We acknowledge the uniqueness of each individual, understanding that their needs and aspirations may differ, as every situation is distinct. Golden Gate Recovery Center is a committed men’s addiction treatment facility that offers a wide range of resources aimed at tackling both addiction and mental health issues.
Situated in the tranquil environment of Marin County, CA, our rehabilitation center ensures a secure and nurturing atmosphere for those pursuing recovery. Golden Gate focuses on uncovering the underlying causes of co-occurring disorders and exploring the connection between addiction and mental health challenges. Always check in with a healthcare provider to get personalized advice and treatment tailored to your specific needs.
We provide dual diagnosis treatment focusing on relieving symptoms and providing strategies to help our clients stop drinking and become sober.

If you’re a man who’s been struggling with alcohol addiction and has developed an alcoholic ulcer as a result, Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, CA can help you or a loved one break free from alcohol’s choke-hold and take the first step towards a healthier life.
Immerse yourself in our expansive and carefully curated programs that are personalized just for your needs as you walk away from addiction and towards control. Say goodbye to the drinks that don’t serve you and hello to a healthier, happier you. With abundant care and support, Golden Gate Recovery’s alcohol rehab center is your go-to spot to pour your focus into a brighter future. Don’t wait for the perfect moment, contact us today and get the ball rolling.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:
It’s a problem when any portion of the brain shrinks. However, the damage done by alcohol is particularly worrying because some of that shrinkage probably comes from cell death. Once brain cells die, the effects are permanent. Fortunately, some of the changes in an alcoholic brain are simply due to brain cells changing size.
Research has shown that the brain can repair itself relatively quickly after ceasing to drink alcohol. The brain’s gray matter shrinks from alcohol abuse, but it begins reversing the damage within two weeks after chronic alcohol abusers stop drinking. When a person with alcohol use disorder (alcoholism) stops drinking, their brain cells return to their normal size. This shows that some alcohol-related brain damage can be reversed.
The timeline for alcohol recovery can be somewhat quick in certain areas, while different areas of the brain recover at different rates. Studies have shown that a lot of the lost functionality in the brain returns quickly. New research reveals that it takes at least 2 weeks for the brain to begin returning to normal, so this is typically the point where the alcohol recovery timeline starts.
You may still be going through some withdrawal symptoms, which makes this period high risk for relapsing. You may feel confused, distracted, and irritable.
That being said, it may take anywhere from a couple of months to several years before you realize cognitive improvements and added cognitive abilities. During this time, you might still have problems with abstract reasoning, short-term memory and visual-spatial ability.
Long-term alcohol use can damage the brain in these ways:

Alcohol use also has some notable short-term effects on the brain including:
Because alcohol mainly affects the frontal lobe which is linked to higher-level thinking, it can lead to poor judgment and impulsive behavior.
Drinking harms the brain’s ability to form new memories, causing “blackouts.”
Alcohol impacts the cerebellum, which is responsible for balance and coordination, causing difficulting walking and clumsiness.
Alcohol can lead to quick mood changes, which may lead to aggression or emotional instability.
Reaction time is slowed down due to impaired brain function when under the influence of alcohol.
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to change its functions and physical structure based on life experiences and repeated thoughts, behaviors, and emotions. Whether it’s good or bad, whatever you do repeatedly is wired into your brain’s structure. That’s why it’s difficult to change a habit or routine.
But new habits can be formed, and neuroplasticity is what makes it possible for people to change behaviors and adapt to changes forced on them. Still, the brain can’t recognize the difference between good or bad experiences or habits. Since the brain learns repeated habits, it can result in development of an addiction.
AUD recovery focuses on changing or replacing the harmful habit of using alcohol with positive, healthy habits. When an individual in recovery develops a positive new habit, the brain changes. It creates a neural (central nervous system) pathway reinforcing the new habit. As the new habit is repeated, the new pathway gets stronger through neuroplasticity while the pathways of the negative habits become weaker since they are no longer being reinforced.
Even after long-term alcohol use, the process of neuroplasticity can help the brain heal itself. This can begin during medical detox, the first step in recovery. The time it takes for the brain to heal itself depends on:
Neurotransmitters are chemicals in the brain that allow neurons in the brain to communicate with each other and are involved in almost every part of everyday life:
When they are disrupted by alcohol they can become blocked or overstimulated so they can’t address normal daily functions. The reward system is designed to strengthen positive experiences (eating, socializing, and sex), so you’ll want to do them more often.
The brain releases dopamine–the “feel good” hormone–every time you have a positive experience so you’ll remember it and repeat it to form a habit. Chronic alcohol usage can alter the function and structure of the brain. This basically hijacks the brain’s reward system and motivates the transition from being an occasional drinker to being dependent on it.
Our brains have a remarkable ability to adapt and repair, even after prolonged AUD. The brain continues to build brain cells and neural pathways , and its ability to adapt allows it to modify, grow and reorganize itself after addiction. But, it takes some time for the brain to repair itself.
The brain needs to be free from the alcohol, or the amount needs to have been drastically reduced. There are many treatment options to help people stop or cut back. Withdrawing or detoxing from alcohol can take a few days to a few weeks depending on:
You can do a lot to help your brain and body recover and improve neuroplasticity and brain health through:
This increases the size of the hippocampus
Mindful meditation can strengthen brain circuits damaged by AUD
This helps to compensate for the vitamin and mineral deficiencies that usually happen with AUD
The brain flushes out toxins while you sleep so good sleep habits can help brain recovery

If you or someone you care about is struggling with AUD, there is help available at Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, CA. We are a gender-specific treatment facility created by men in long-term recovery for men who need support and comprehensive treatment for alcohol use disorder, or any addiction.
We are set up to design individualized care for each client and an appropriate continuum of care. Our facility can offer you:
Golden Gate has 3 outpatient programs ranging in duration and intensity.
Golden Gate Recovery is has licensed and experienced clinicians and addiction specialists whose only job is to help you recover. Contact us today. Find out why we have the Gold Seal of Approval from The Joint Commission, a non-profit organization that accredits healthcare organizations.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Delirium tremens (DTs) is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition that can develop in individuals who are dependent on alcohol and suddenly stop drinking. Understanding how long delirium tremens lasts is crucial for managing this dangerous phase of alcohol withdrawal. DTs typically begin within 48 to 96 hours after the last drink and can last anywhere from 3 to 7 days, though some severe cases may persist longer. The duration of DTs depends on factors like the severity of alcohol dependence, the presence of underlying health issues, and the timeliness of medical intervention.
Proper medical supervision is essential during this period, as untreated delirium tremens can result in significant complications, including seizures, heart failure, and even death. For those experiencing DTs, professional alcohol detox and treatment are critical for ensuring safety and improving the chances of recovery.

Delirium tremens is the most severe form of alcohol withdrawal. It is characterized by sudden and extreme nervous system disturbances, such as confusion, hallucinations, severe shaking, agitation, and fever. DTs typically affect people who have been drinking heavily for a long time and abruptly stop or dramatically reduce their alcohol consumption. The condition is a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention due to the high risk of serious complications.
Alcohol suppresses the brain’s natural ability to stimulate certain neurotransmitters, which leads to chemical imbalances when a person abruptly stops drinking. The brain overcompensates by releasing excessive excitatory neurotransmitters, causing the hyperactivity seen in delirium tremens. This rapid chemical change can overwhelm the body, triggering dangerous symptoms.
Delirium tremens is relatively rare compared to other forms of alcohol withdrawal, but when it does occur, it is extremely serious. According to medical research, about 5% of people who experience alcohol withdrawal develop DTs. However, the likelihood of developing delirium tremens increases for those with a long history of alcohol abuse, those who have experienced DTs in the past, or those with certain health conditions like liver disease.
While DTs may not be common among the general population, the fact that they can be fatal underscores the importance of recognizing early symptoms and seeking immediate medical care for those undergoing alcohol detox.
Delirium tremens is caused by the brain’s severe reaction to the sudden absence of alcohol after a long period of heavy drinking. People who experience DTs have often developed physical alcohol dependence, meaning their bodies have become accustomed to its presence to function normally.
Symptoms of delirium tremens include:
These symptoms can escalate quickly, making it crucial for anyone going through alcohol withdrawal to be monitored by medical professionals, particularly in the first few days after stopping alcohol use.
There is no exact threshold for how much alcohol one must consume to develop DTs. However, it typically affects those who have been drinking heavily for an extended period—often several years. Chronic heavy drinking is defined as consuming more than 8 drinks per week for women and more than 15 drinks per week for men.
Additionally, individuals who consume alcohol in excessive quantities daily, particularly those who drink large amounts of liquor, are at greater risk. People with a previous history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms or delirium tremens are more susceptible, as are those who binge drink frequently.
Delirium tremens usually start 2 to 3 days after the last drink, but in some cases, it can be delayed up to a week. The acute phase of DTs typically lasts about 3 to 7 days. During this time, the most severe symptoms—such as hallucinations, seizures, and confusion—are likely to occur.
Even after the most intense symptoms subside, individuals may continue to experience lingering issues like fatigue, anxiety, and insomnia for weeks or months. Medical professionals need to be involved in the detox process to ensure the patient’s safety and provide the necessary support for long-term recovery.

Several factors increase the risk of developing delirium tremens, including:
Yes, delirium tremens can be fatal if left untreated. Mortality rates for untreated DTs range from 5% to 15%. Severe symptoms like seizures, heart arrhythmias, and respiratory failure are the most life-threatening aspects of the condition. Prompt medical treatment significantly reduces the risk of death, with modern medical care lowering mortality rates to around 1-2%.
Even in cases where death is not a direct outcome, complications from DTs can cause long-term health issues. People who experience DTs are also at a higher risk of developing cognitive impairments or mental health disorders due to the stress placed on the brain during withdrawal.

Diagnosis of delirium tremens is typically based on a patient’s medical history, symptoms, and physical examination. Healthcare professionals assess signs like confusion, agitation, shaking, and hallucinations to determine the severity of alcohol withdrawal. Blood tests may be used to assess electrolyte levels and liver function, which are often impaired in heavy drinkers.
A doctor might also inquire about the patient’s alcohol consumption habits, previous withdrawal symptoms, and any co-occurring medical conditions. Early diagnosis is critical to prevent the condition from escalating to a life-threatening level.
Treatment for delirium tremens takes place in a medical facility, typically in a hospital or specialized detox center. The goals of treatment are to prevent seizures, stabilize the patient’s vital signs, and manage symptoms of withdrawal. Common treatments include:
After the acute phase of treatment, patients are encouraged to seek ongoing care for alcohol use disorder, such as inpatient or outpatient treatment, to prevent future relapses and manage long-term recovery.
After overcoming delirium tremens, long-term recovery from alcohol addiction requires comprehensive treatment that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of addiction. Alcohol use disorder is a chronic condition that benefits from a multi-faceted approach, including:
At Golden Gate Recovery, we provide comprehensive treatment to help men overcome alcohol addiction. Our detox program is equipped to safely manage withdrawal symptoms, including delirium tremens, under medical supervision. After detox, we offer a range of outpatient services tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual.
We also provide sober living options and dual diagnosis treatment, addressing co-occurring mental health disorders like anxiety, depression, and trauma. Our goal is to help you build a strong foundation for long-term recovery and reclaim your life from addiction. If you or a loved one is struggling with alcohol use disorder, reach out to Golden Gate Recovery today and take the first step toward lasting recovery.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Alcohol consumption can have an impact on various bodily systems, including the immune system. This relationship is important to understand as it affects overall health and well-being. Golden Gate Recovery recognizes the significance of addressing alcohol’s effects within a comprehensive treatment plan. Their approach integrates evidence-based practices to promote healthier lifestyle choices while supporting individuals’ recovery journeys.
By focusing on long-term wellness, Golden Gate Recovery aims to equip individuals with the tools and knowledge necessary for maintaining balance and reducing potential risks associated with alcohol use. The recovery process emphasizes education, personal growth, and professional support to guide individuals toward a healthier future.
Alcohol consumption can influence the gut biome, which is important in maintaining overall health. The balance of bacteria in the gut is essential for digestion, immune function, and other bodily processes. When this balance is disturbed, it can result in a range of health issues.
At Golden Gate Recovery, the connection between alcohol use and gut health is addressed as part of a holistic treatment plan. Individuals are better equipped to achieve sustainable recovery by promoting healing and supporting gut balance. We offer personalized care that focuses on restoring both physical and emotional well-being, providing a pathway to improved health and lasting sobriety.
Autoimmune diseases happen when the immune system mistakenly targets and attacks the body’s healthy cells, tissues, or organs. Instead of protecting the body from harmful invaders like viruses and bacteria, the immune system targets normal cells, leading to inflammation and damage. Autoimmune diseases come in various forms, each impacting different areas of the body.
Examples of autoimmune disorders include conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. Managing these conditions often requires medical intervention to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Early detection and treatment are important for managing autoimmune diseases, helping to control the immune system’s response, and limiting long-term effects on the body.
The immune system is the body’s defense mechanism, designed to protect against harmful invaders such as viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens. It is made up of two primary components: the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. The innate system is the body’s first line of defense, responding quickly to potential threats by recognizing general signs of danger. The adaptive system, on the other hand, is more specialized, developing a targeted response to specific pathogens that the body has previously encountered.
Key players in the immune system include white blood cells, antibodies, and lymph nodes. Together, they identify, attack, and eliminate harmful substances. When functioning properly, the immune system keeps the body healthy.
A healthy immune system is essential for protecting the body against infections, diseases, and harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses. It helps the body recognize and eliminate these threats before they cause significant harm, keeping you well and able to recover quickly from illnesses.
Beyond fighting off external dangers, a well-functioning immune system also maintains internal balance, preventing issues like chronic inflammation and autoimmune disorders, where the body mistakenly attacks its tissues. When the immune system is compromised, the body becomes more vulnerable to infections, prolonged illness, and other health complications. Maintaining immune health is vital for overall well-being and long-term vitality.

Drinking alcohol can have significant effects on individuals with autoimmune diseases. Alcohol has the potential to weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to manage autoimmune responses. For those already living with conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or multiple sclerosis, alcohol consumption can worsen symptoms and contribute to inflammation. Drinking alcohol excessively may interfere with medications used to treat autoimmune diseases, reducing their effectiveness and increasing the risk of side effects.
At Golden Gate Recovery, the relationship between alcohol use and autoimmune disease is considered as part of personalized treatment plans. Their holistic approach focuses on supporting individuals in managing their health conditions while addressing the impact of alcohol on overall well-being and recovery.
Binge drinking, defined as consuming large amounts of alcohol in a short period, poses serious health risks. It can lead to immediate dangers such as accidents, alcohol poisoning, and impaired judgment. Over time, binge drinking increases the risk of developing chronic conditions like liver disease, heart problems, and mental health issues. It also affects personal relationships, work, and academic performance, and can contribute to long-term alcohol dependency.
The physical toll of binge drinking is not limited to the liver and heart; it can also weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections. Addressing binge drinking early can prevent these risks and support better overall health outcomes.
Alcohol affects the immune system by impairing its ability to respond to infections and illnesses. Regular or excessive drinking can reduce the production of white blood cells, weakening the body’s defense against harmful pathogens. Alcohol also disrupts the gut barrier, allowing harmful bacteria to enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation. This inflammation can weaken immune responses, making it harder for the body to fight off infections.
Over time, alcohol can contribute to chronic conditions that further compromise immune function. Those who consume alcohol regularly may experience slower recovery from illnesses, leaving them more vulnerable to both acute infections and long-term health issues.
Alcohol can affect autoimmune diseases by altering the immune system’s balance. Regular consumption may disrupt the production of cytokines, proteins that regulate immune responses, leading to an exaggerated inflammatory response.
Additionally, alcohol can interfere with the normal functioning of immune cells, which are crucial for controlling autoimmune flare-ups. For individuals with autoimmune diseases, this disruption can lead to more frequent and severe symptoms. Alcohol can also impact gut health, further affecting immune system balance and potentially aggravating autoimmune conditions. Managing alcohol intake is important for maintaining stability in autoimmune disease management and overall health.
Alcohol can interact with medications used to treat autoimmune diseases, potentially affecting their effectiveness and safety. Many autoimmune medications, such as immunosuppressants and corticosteroids, may have their side effects worsened by alcohol. This can lead to increased risks of gastrointestinal issues, liver damage, and compromised immune function. Alcohol can interfere with the metabolism of these drugs, causing unpredictable levels in the bloodstream and reducing their effectiveness.
For those with autoimmune diseases, it’s important to discuss alcohol consumption with a healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions and ensure effective management of their condition.
Heavy drinking can have profound effects on the body, impacting multiple systems. It can cause liver damage, which may include conditions such as fatty liver, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. The heart can suffer from high blood pressure, cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmias. Heavy drinking also weakens the immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections and illnesses. It can impair cognitive function, leading to memory problems and changes in behavior.
Heavy alcohol use can contribute to gastrointestinal issues, such as ulcers and pancreatitis, and increase the risk of certain cancers. Long-term heavy drinking disrupts overall health, making it harder for the body to function properly and recover from illnesses.
When you quit drinking, the immune system begins to recover and improve its functionality. Initially, reducing alcohol intake allows the immune system to start repairing itself, restoring the balance of immune cells, and reducing inflammation. Over time, the body becomes more effective at fighting infections and managing autoimmune responses. The gut barrier also starts to heal, which helps reduce systemic inflammation and improves overall immune health.
While recovery can vary based on individual factors and the extent of previous damage, many people experience significant improvements in immune function after quitting alcohol. Overall, abstaining from alcohol supports the immune system’s ability to maintain health and resist illnesses more effectively.

Choosing a reputable men’s alcohol rehab facility is essential for effective recovery. Golden Gate Recovery is known for its commitment to personalized care and evidence-based treatments. They offer tailored programs that address the unique needs of men struggling with alcohol use, combining medical support with addiction therapy services. This approach helps individuals develop coping strategies, understand the root causes of their addiction, and work towards sustainable recovery.
Trusting a facility like Golden Gate Recovery ensures access to experienced professionals and a supportive environment, both of which are necessary for overcoming addiction and achieving long-term sobriety. The focus on personalized care helps set a solid foundation for lasting recovery.
If you’re struggling with alcohol and need support to quit, Golden Gate Recovery can help. Their specialized programs are designed to address the unique challenges of overcoming alcohol addiction. With a focus on personalized care, they provide evidence-based treatments and therapeutic support to guide you through the recovery process.
The experienced team at Golden Gate Recovery is dedicated to helping individuals achieve lasting sobriety and rebuild their lives. If you’re ready to take the first step toward recovery, contact us to learn more about how we can assist you in your journey to a healthier, alcohol-free life.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:
Have you ever wondered if someone you know might be struggling with alcohol abuse, even though they seem to have it all together? Functional alcoholism is a sneaky problem that can often go unnoticed, especially when someone appears to be managing their daily responsibilities just fine. It’s easy to overlook the signs when everything on the surface seems normal. However, understanding the subtle indicators of functional alcoholism can make a big difference in recognizing when help is needed.
At Golden Gate Recovery, we specialize in helping individuals uncover and address the hidden challenges of functional alcoholism. Our compassionate and experienced team is here to support you or your loved ones every step of the way. In this article, we’ll explore what functional alcoholism looks like, and how to recognize the signs and the consequences of being a high-functioning alcoholic. Let’s dive in with understanding and empathy, knowing recovery is possible with the right guidance and support.
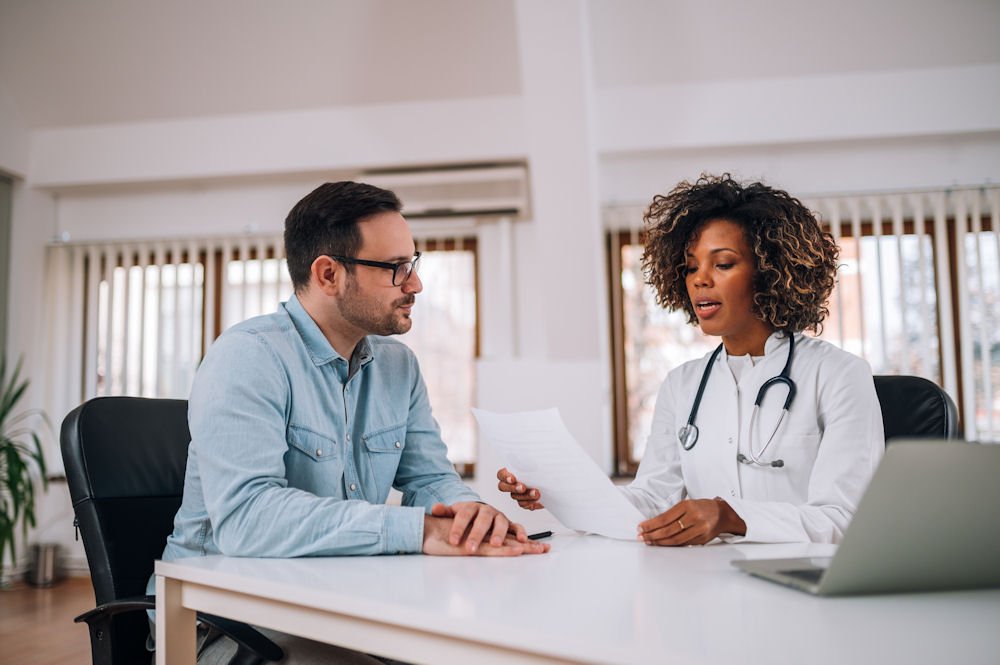

High-functioning alcoholism is a term used to describe individuals who appear to maintain a relatively normal and productive life while engaging in alcohol use disorder. These individuals often hold down jobs, maintain relationships, and handle daily responsibilities effectively, making it difficult for others to recognize the extent of their alcohol problem.
Despite the outward appearance of control, high-functioning alcoholics are still struggling with addiction and the negative consequences it brings. Alcohol use disorder affects their health, relationships, and overall well-being, even if these issues are not immediately visible to those around them.
Recognizing the signs of high-functioning alcoholism in yourself or a loved one can be challenging due to the ability of these individuals to hide their problems. Here are some indicators that might suggest functional alcoholism:
Beyond the personal indicators, there are additional signs to watch for in someone you suspect might be a high-functioning alcoholic. Here are some things to think about asking:
Recognizing these signs early can be crucial to addressing the issue before it escalates. If you notice these behaviors in someone you care about, it may be time to have a compassionate conversation and encourage them to seek professional help. Support from friends and family can make a significant difference in their journey toward recovery.
The difference between high-functioning and non-high-functioning alcoholism mainly lies in how much control and stability a person appears to have. Non-high-functioning alcoholics often have visible problems with their drinking, such as losing jobs, facing legal issues, and having strained relationships. On the other hand, high-functioning alcoholics seem to live normal lives, which can make it harder to see their drinking problem and get help.
It’s important to remember that high-functioning alcoholism is just as serious. Even though they seem to have everything under control, high-functioning alcoholics face the same health risks and struggles as those with more obvious drinking problems. This can be dangerous because it allows the addiction to grow unnoticed, making it harder for friends and family to spot the issue and offer help.

A high-functioning alcoholic (HFA) may not fit the stereotypical image of an alcoholic. They often maintain a façade of normalcy, successfully managing their professional and personal responsibilities. However, their drinking patterns and behaviors can provide clues to their underlying issues. Here’s what the drinking habits of a high-functioning alcoholic might look like:
A high-functioning alcoholic (HFA) may drink daily or almost daily, often spreading out their intake to avoid noticeable intoxication. They usually have a high tolerance for alcohol and may establish routines, such as having a drink after work or with dinner. Their drinking often occurs in social settings where alcohol consumption is normalized.
HFAs might hide their drinking from certain people, drink in secret, or lie about their intake. They often maintain jobs and relationships, rationalizing their drinking as a reward or a necessity for stress management. They tend to downplay their problem, comparing themselves to more stereotypical alcoholics and denying the impact on their health and well-being.
Over time, HFAs may develop health issues like liver damage or high blood pressure. They might experience mood swings, irritability, or anxiety, especially when unable to drink. Frequent blackouts or memory lapses, even if minor, can also occur.
Relationships with family and friends may become strained, and HFAs might face legal issues such as DUIs. Their work performance may fluctuate due to hangovers or the effects of drinking. Despite maintaining appearances, consistent patterns of heavy drinking and its toll can reveal their underlying issues.
Being a high-functioning alcoholic can have several significant consequences, both for the individual and those around them. While such individuals might appear to manage their professional and personal responsibilities, the underlying addiction can lead to various negative outcomes:

If you or a loved one is struggling with high-functioning alcoholism, seeking professional help is crucial. Golden Gate Recovery’s Men’s Alcohol Rehab Center offers specialized programs designed to address the unique challenges faced by high-functioning alcoholics. Our comprehensive approach includes:
Our alcohol rehab center in California provides a supportive and nurturing environment for recovery. Our experienced team is dedicated to helping you or your loved one achieve lasting sobriety and regain control of life. Contact us today!
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for: