
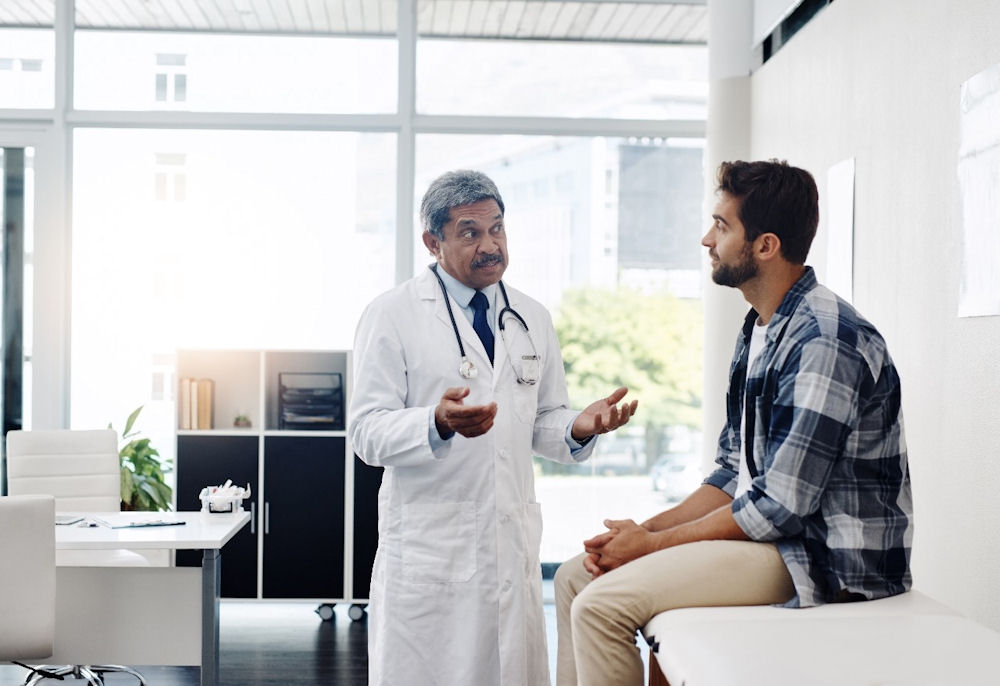
In recent years, microdosing, taking very small, sub-perceptual amounts of psychedelic substances such as LSD or psilocybin, has gained widespread attention. Many proponents claim it can boost creativity, improve focus, reduce anxiety, or enhance overall mood without producing the hallucinogenic effects associated with larger doses. These claims have been widely shared on social media, in tech circles, and in popular culture, contributing to the perception that microdosing is a safe, low-risk practice.
However, scientific research on microdosing is still in its early stages, and the long-term effects are largely unknown. Emerging studies and anecdotal reports suggest that even small, repeated doses can carry mental, emotional, and physical risks. Some individuals may experience heightened anxiety, mood instability, cognitive disturbances, or unintended interactions with other medications or pre-existing health conditions. Beyond individual health concerns, there is also the potential for dependence, social consequences, or the disruption of healthy coping mechanisms.
At Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, California, located in Marin County, we are committed to helping individuals understand the full spectrum of risks associated with microdosing. By providing evidence-based addiction treatment and comprehensive support, we aim to empower people to make informed decisions about their mental and physical well-being and to recognize when professional guidance may be needed.
If you’re in recovery from substance use, microdosing carries risks beyond what’s unknown for everyone else. Since microdosing works by altering mental state and brain chemistry, it can potentially trigger relapse or interfere with established recovery processes.
Research shows real safety concerns, including cardiovascular risks, potential for psychological dependence, and effects on brain chemistry we do not fully understand, especially in people whose neurotransmitter systems are already vulnerable from past addiction.

Microdosing refers to taking very small amounts of psychedelic substances, typically one-tenth to one-twentieth of a recreational dose. The practice aims to produce subtle changes in mood, focus, or creativity without causing hallucinations. Common substances include psilocybin (0.1-0.3 grams dried material), LSD (10-25 micrograms), and, less commonly, MDMA or DMT.
While wellness communities often promote microdosing as a natural treatment for depression and anxiety, the science doesn’t back up these claims, as typical microdosing practices lack medical standards or accepted protocols. Initially, microdosing may lead to reductions in depression and stress, but over time, neuroticism can increase, a sign that the body is developing tolerance. As the initial effects begin to fade, some individuals increase the dose to keep feeling the euphoric effects. This pattern can ultimately contribute to dependency and, in some cases, addiction.
Microdosing and recreational use differ in intent and dose, but smaller amounts don't guarantee safety. Research shows microdosing may create psychological dependencies, even at sub-perceptual doses. Studies show perceived benefits often fade after this initial period, yet individuals may continue to pursue earlier effects.
Microdosing substances can create dangerous interactions with medications used in recovery. Psychedelics affect serotonin pathways, leading to serious complications when combined with SSRIs and MAOIs.
Psilocybin typically metabolizes within 24-48 hours. Detection windows vary based on metabolism, dosage, frequency, and test type. Most abstinence-based programs classify psychoactive substance use, including microdosing, as a relapse, regardless of dose or intention.
Open communication with treatment providers represents the most important step. Medical professionals can assess individual risk factors, including medication interactions and addiction history.

Understanding why people try microdosing doesn’t mean it works. In controlled studies with placebos, microdosing doesn’t perform better than sugar pills. Much of what people report comes down to expecting it to work.
Common motivations include self-medication for depression or anxiety, believing it might accelerate recovery, curiosity about alternative approaches, and peer influence from social media trends. The biggest risk? Triggering relapse. Microdosing changes mental state—the same mechanism that can trigger behaviors leading to relapse.
A landmark study found microdosing didn't improve depression scores—contradicting anecdotal reports. In a 4-week self-blinding trial with 191 participants, the microdose group showed improvements in well-being and mindfulness from baseline to week 5. But these improvements weren't better than a placebo. Only decreased neuroticism persisted at week 9 follow-up, suggesting limited long-term effects of microdosing.
Microdosing is heavily marketed through wellness culture as a "biohack." For people in recovery, these messages land at vulnerable times. The gap between what people believe about microdosing and what science shows requires honest conversations separating hype from validated research.

Recovery isn’t just about avoiding obvious relapses. Subtle shifts, such as rationalizing substance use and building routines around chemicals, can wreck stability even when the substance seems harmless. Treatment participation may become inconsistent when individuals prioritize microdosing over therapy sessions.
Most studies span only 4-6 weeks, with a few extending beyond. Psychological improvements fade after about four weeks, while risks like increased neuroticism and anxiety can emerge. Many studies include fewer than 100 participants, which is too small to detect real effects. When studies use proper controls, microdosing doesn't beat sugar pills.
Psychedelics don't create physical addiction like alcohol and opioids, but microdosing can reinforce addiction patterns. Using any substance to regulate mood represents core addiction behavior. Reliance on microdosing rituals creates psychological dependence; individuals may feel unable to function without regular doses.
Microdosing increases relapse risk by lowering psychological barriers to "using something" and weakening mental frameworks supporting abstinence. Even small psychoactive doses can trigger cravings through stress, sleep disruption, or emotional volatility. Research confirms the potential to trigger relapse as the most immediate concern with microdosing in recovery.

Online claims about microdosing aren’t supported by research. In controlled studies with placebos, reported benefits don’t beat sugar pills. Only about 20 experimental studies exist, full of contradictions and methodological problems.
Smaller doses don't automatically mean safety. Research documents adverse effects, including increased anxiety, irritability, restlessness, headaches, and sleep disturbances. Over 6 weeks, 98 microdosers showed reduced depression and stress but increased neuroticism.
Microdosing doesn't address what drives substance use. Recovery means processing trauma, managing depression and anxiety, building coping skills, and understanding relapse patterns. Established treatments like cognitive-behavioral therapy and dialectical behavior therapy have demonstrated efficacy, while microdosing benefits remain unproven.
Natural origin doesn't guarantee safety. Psilocybin mushrooms can cause harm, interact with medications, or trigger psychological destabilization. The FDA doesn't regulate microdosing substances; there's no quality control. Without regulation, individuals risk contamination and inconsistent potency.

Most studies last only 4-6 weeks. Few investigations extend beyond this, and those that do often lack proper controls. Psychological improvements fade after about four weeks. A phase 2 study examined daily psilocybin microdoses (1-3 mg over three weeks) in patients with advanced illness. Researchers saw drops in psychological distress, but effects faded after four weeks, a pattern seen across multiple studies.
Microdosing can interact with psychiatric medications like SSRIs and MAOIs. Antidepressants and antipsychotics alter neurotransmitter levels such as serotonin and dopamine. Adding psychedelics affecting the same brain systems can cause unpredictable problems: increased anxiety, unstable mood, or medications that stop working effectively.
Most psychedelics are illegal. Getting caught can cost an individual their employment, housing, family relationships, or treatment placement. Unregulated products may contain wrong doses, adulterants, or contamination.
There’s no long-term data that shows microdosing won't cause tolerance, dependence, or brain damage over time. Current trials highlight safety gaps: psychological dependence, worse anxiety, physical discomfort, trouble focusing, and impaired driving. No large-scale studies have examined microdosing for addiction recovery.

Research shows psychological dependence can develop when relying on any substance to function, even at barely perceptible doses. Microdosing can maintain patterns where you reach for chemical fixes when emotions become difficult.
Microdosing reinforces reaching for substances when uncomfortable. When a person microdoses because they are stressed, their brain connects relief with taking something, which is the same pattern seen in dependence. A survey of 263 microdosers found expected benefits mismatched actual outcomes, with limited residual effects on non-dosing days.
Psychological dependence develops when individuals believe they cannot function without microdosing. In recovery, this erodes confidence in sober coping skills. A 4-week self-blinding trial showed improvements weren't superior to placebo, with decreased neuroticism persisting only at week 9 follow-up. Scientists don't fully understand the long-term effects of microdosing on brain chemistry.
Microdosing may conflict with recovery goals by undermining abstinence commitments and reintroducing substance use as a coping strategy. Creating secrecy around microdosing compromises therapeutic relationships built on transparency. The most immediate concern remains the potential to trigger relapse.

Microdosing is framed as a mental health tool, but mental health conditions increase risks. For people with co-occurring disorders, stability and predictability matter most. Research shows microdosing can both increase and decrease mood, anxiety, and attention, making outcomes unpredictable.
Claims about microdosing mushrooms for depression and anxiety are common, but findings often match placebo-driven improvements. A landmark study found microdosing didn't improve depression scores. Some individuals experience worsened anxiety, irritability, or sleep disruption. These issues can intensify over time, particularly when effects diminish after 4 weeks.
People with bipolar disorder who have a history of psychosis, severe anxiety, or significant trauma may face heightened risks of mood destabilization or worsening symptoms. Integrated dual diagnosis treatment offers evidence-based approaches with known benefit-risk profiles.
Mixing psychedelics with psychiatric medications creates unpredictable effects. Medical supervision is essential before making changes when taking antidepressants or mood stabilizers. No conclusive long-term safety data confirms absence of tolerance, dependence, or cumulative neurotoxicity.

When microdosing feels appealing because symptoms persist, additional support may benefit more than experimentation. Golden Gate Recovery provides evidence-based treatment designed for long-term recovery and mental health stability.
Recovery goals like mood improvement, clarity, and motivation can be achieved through evidence-based approaches carrying no legal risks, no unknown long-term effects of microdosing on brain chemistry, and no relapse potential.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy and dialectical behavior therapy address cravings, emotional regulation, relapse prevention, and distress tolerance. Studies show microdosing improvements often diminish after four weeks, while evidence-based therapies build lasting skills.
Substance-free wellness approaches improve mood without relapse risk. Golden Gate Recovery incorporates holistic therapy elements addressing the same goals individuals seek through microdosing.
Professional guidance prevents avoidable harm, particularly during early recovery or when taking prescribed medications. Clinicians evaluate risks, medication interactions, and symptom patterns while offering evidence-supported alternatives.
The long-term effects of microdosing remain largely unknown, with most studies spanning only 4-6 weeks. Research shows psychological improvements fade after approximately four weeks, while potential risks like heightened neuroticism may persist.
Evidence-based treatment offers a clearer, safer path. Established therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy have demonstrated efficacy, while microdosing benefits remain unproven. Golden Gate Recovery supports adult men facing addiction and co-occurring mental health challenges with structured, professional care. To explore your options, contact us today.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

When we overcome one addiction, we might think the battle is over. However, sometimes we simply trade one addiction for another without realizing it. This is called transfer addiction, and it’s a challenge many people face during recovery. At Golden Gate Recovery, we see this pattern frequently and have developed specialized approaches to help men recognize and address addiction transfer before it takes root.
Transfer addiction can happen to anyone in recovery, regardless of their original addiction. Understanding this phenomenon helps us create more effective, long-lasting recovery plans for our clients. In this article, we’ll explore what transfer addiction is, how it develops, and most importantly, how to prevent it from derailing recovery.
Transfer addiction, also known as addiction transference, cross-addiction, or addiction replacement, occurs when someone in recovery replaces one addiction with another. Instead of fully overcoming the original addiction, the person begins relying on a new substance or behavior to cope with life’s challenges.
This replacement can involve substances like alcohol, prescription medications, or illegal drugs. It can also involve behaviors such as gambling, shopping, exercise, or even addiction in the workplace. The key characteristic is that the new behavior becomes compulsive and starts to negatively impact daily life.
Research from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) suggests that approximately 20-30% of people in recovery may experience some form of addiction transfer. The risk is particularly high during the first year of recovery when coping mechanisms are still developing. Key points about transfer addiction include:

Transfer addiction develops because addiction fundamentally changes how our brain’s reward system works. When we stop using our primary substance or behavior, our brain still craves the dopamine release it once received. This can lead us to seek out new ways to experience pleasure or relief from discomfort. The process typically follows this pattern:
According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), several factors increase the risk of developing transfer addiction:
The National Institute on Drug Abuse explains that addiction changes neural pathways in our brain, making us more susceptible to other addictions even after the original substance is no longer used.
Transfer addiction is widespread after bariatric (weight-loss) surgery. When food can no longer be used as a coping mechanism, some people turn to alcohol, shopping, gambling, or other behaviors to fill the emotional void.
A 2021 study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that the risk of developing alcohol use disorder increased by 50% following bariatric surgery. This suggests that when one form of comfort (food) becomes unavailable, the brain may seek alternatives.
Common examples of transfer addiction include:
| Original Addiction | Common Transfers | Why It Happens |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | Gambling, sex addiction, and food | Similar dopamine response, seeking excitement |
| Opioids | Benzodiazepines, alcohol, and food | Seeking relief from physical/emotional pain |
| Food | Shopping, alcohol, exercise | Looking for alternative comfort or control |
| Work | Exercise, gambling, internet | Seeking achievement or escape |
After bariatric surgery, the body physically cannot consume large amounts of food. While this helps with weight loss, it also removes a primary coping mechanism for many people. According to the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, up to 20% of patients may develop problematic alcohol use after surgery. This happens because:
Other common patterns of transfer addiction include:
These transfers occur because the underlying emotional needs driving the original addiction haven't been addressed. The person simply finds a new way to cope with those same feelings.

Recognizing transfer addiction early can help prevent it from becoming as problematic as the original addiction. The signs often appear gradually and may be difficult to identify at first.
In men specifically, transfer addiction may show up as:
These signs mirror those of the original addiction, though they might be subtler at first. The person may also believe they’re “doing better” because they’re no longer engaging in their primary addiction.
Preventing transfer addiction requires awareness and proactive strategies. The good news is that with the right approach, we can significantly reduce the risk.
Building a toolkit of healthy coping mechanisms is essential for preventing transfer addiction. These skills help us manage stress, process emotions, and find healthy sources of pleasure. Effective coping skills include:
Research from the National Institutes of Health shows that people who develop multiple healthy coping strategies have a significantly lower risk of developing transfer addiction.
Understanding what triggers cravings or urges helps us respond more effectively. Common triggers include:
By identifying these triggers, we can develop specific strategies to handle them without turning to addictive behaviors.
Comprehensive treatment that addresses both addiction and any underlying issues is crucial for preventing transfer addiction. Evidence-based approaches include:
At Golden Gate Recovery, we emphasize addressing the root causes of addiction, not just the symptoms. This holistic approach helps prevent the cycle of addiction transfer.

When transfer addiction does develop, effective treatment is available. The approach is similar to treating the original addiction, but with added focus on the pattern of transfer.
Several therapeutic approaches have proven effective for addressing transfer addiction:
These approaches work by helping us understand the function of the addictive behavior in our lives and develop healthier alternatives.
Support groups specific to different types of addiction provide understanding and accountability. Examples include:
These communities offer the wisdom of shared experience and provide ongoing support beyond formal treatment.
Long-term recovery requires ongoing support. According to SAMHSA, people who participate in aftercare programs are up to 50% more likely to maintain their recovery long-term. Effective aftercare includes:
The transition from formal treatment to independent recovery is when many people are vulnerable to transfer addiction, making aftercare particularly important during this time.

Recovery is about more than just stopping an addictive behavior; it’s about creating a fulfilling life that doesn’t require escape through substances or compulsive behaviors. To minimize the risk of transfer addiction, we can:
Recovery is a lifelong journey, not a destination. By staying vigilant about the risk of transfer addiction and continuing to develop healthy coping skills, we can build a sustainable recovery that addresses our needs in healthy ways.
Transfer addiction is caused by changes in the brain's reward system and unresolved psychological issues that lead people to seek new ways to experience pleasure or escape discomfort during recovery.
Studies indicate that 20-30% of people in recovery may experience some form of transfer addiction, with the risk being highest during the first year of sobriety.
Yes, transfer addiction can often be prevented through comprehensive treatment that addresses underlying issues, develops healthy coping skills, and provides ongoing support.
Treatment includes therapy to address emotional eating, support groups specific to post-bariatric patients, and the development of healthy coping mechanisms to replace food-related comfort.
Transfer addiction refers to replacing one addiction with another over time, while cross-addiction typically means being addicted to multiple substances or behaviors simultaneously.
Yes, transfer addiction can often be prevented through comprehensive treatment that addresses underlying issues, develops healthy coping skills, and provides ongoing support.
If you or someone you love is experiencing signs of transfer addiction, reaching out for help is an important first step. At Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, CA, we specialize in helping men address both primary addictions and the transfer addictions that sometimes develop during recovery. Our comprehensive approach focuses on healing the whole person, not just eliminating specific behaviors.
Contact us today to learn more about our programs and how we can support your journey to lasting recovery.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Methamphetamine use affects the body in many ways, with hair loss being one of the less discussed but still concerning side effects. At Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, California, we often see clients struggling with the physical effects of substance use alongside their addiction.
Hair loss can be particularly distressing as it affects appearance and self-image during an already challenging time. Our comprehensive treatment programs, including our meth addiction treatment center, address both the addiction itself and these physical consequences, helping individuals heal completely as they work toward recovery.
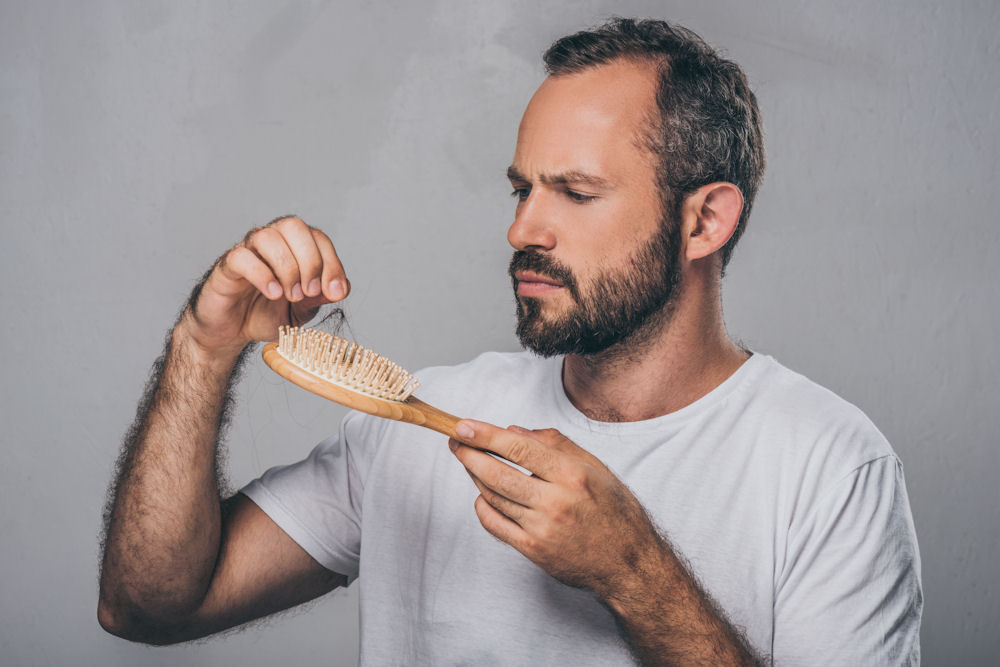
Yes, methamphetamine use can cause hair loss through several different pathways. While meth doesn’t directly attack hair follicles like some medications do, it creates conditions in the body that make hair loss much more likely.
People who use meth often experience thinning hair across their entire scalp rather than in specific patterns. This diffuse hair loss happens because meth affects the whole body, not just certain areas.
Recent studies show that up to 70% of long-term meth users report noticeable hair thinning or loss. This is just one of many physical changes that can occur with regular meth use.
Key point: Hair loss from meth use happens mainly through indirect effects on the body rather than the drug directly damaging hair follicles.

Methamphetamine causes hair loss through multiple pathways that work together. Understanding these mechanisms helps explain why hair problems are so common among people who use meth.
Meth strongly suppresses appetite, often leading to severe malnutrition. When someone uses meth, they might go days with little or no food, depriving their body of nutrients essential for hair growth.
According to research from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, meth users typically consume 40-60% fewer calories than needed for normal bodily functions. This severe nutritional deficit forces the body to prioritize vital organs over "non-essential" functions like hair growth.
When the body lacks these nutrients, a condition called telogen effluvium can develop. This pushes hair follicles prematurely into the resting and shedding phase of the hair growth cycle, resulting in noticeable hair loss.
Key point: Meth-induced malnutrition deprives hair follicles of essential nutrients, forcing more hair into the shedding phase.
Meth places extreme stress on virtually every system in the body. The drug causes dramatic spikes in heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature while disrupting normal sleep patterns.
This physical stress triggers the release of cortisol, often called the "stress hormone." Studies from the Journal of Investigative Dermatology show that elevated cortisol levels can directly damage hair follicles and disrupt the normal hair growth cycle.
The emotional stress of addiction further compounds these effects. Many people using meth experience anxiety, paranoia, and mood swings that keep stress hormones elevated almost constantly.
Sleep deprivation, which is extremely common with meth use, adds another layer of stress. During normal sleep, the body repairs tissues and balances hormones – processes that support healthy hair growth.
Key point: Chronic stress from meth use pushes more hair follicles into the resting/shedding phase while preventing normal repair processes.
Meth often triggers or worsens compulsive behaviors that can directly damage hair and scalp.
One such behavior is trichotillomania, a condition where people feel strong urges to pull out their own hair. Research from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) indicates that stimulant drugs like meth can trigger or worsen this condition.
Many meth users also experience formication – the sensation of insects crawling on or under the skin. This often leads to excessive scratching, picking, and digging at the scalp, damaging hair follicles and creating wounds that can become infected.
Poor hygiene is another common issue during meth addiction. Infrequent washing can lead to scalp buildup, inflammation, and follicle damage, while harsh washing when it does occur can break already weakened hair.
Key point: Meth-induced compulsive behaviors can cause physical trauma to hair follicles, leading to hair loss beyond what's caused by nutritional and stress factors.
The good news is that hair loss from meth use is often reversible once a person stops using the drug and begins recovery. The body has remarkable healing abilities when given proper support and time.
Several factors influence whether and how completely hair will regrow:
Most people begin to see new hair growth within 3-6 months after stopping meth use and addressing nutritional deficiencies. Complete regrowth typically takes 12-18 months with proper nutrition and care.
| Factor | Reversible Hair Loss | Potentially Permanent Hair Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Duration of Meth Use | Short-term | Long-term, chronic |
| Nutritional Deficiency | Mild/moderate | Severe, prolonged |
| Follicle Damage | No scarring | Scarring, permanent damage |
Age | Younger | Older |
Key point: Most meth-induced hair loss is reversible with proper treatment and recovery, though the timeline varies based on individual factors.
Understanding how other substances affect hair helps provide context for meth’s effects.
Like meth, cocaine can cause hair loss through stress pathways and nutritional deficiencies, and those seeking a comprehensive approach often consider a cocaine addiction treatment center. As a stimulant, cocaine increases cortisol levels and can suppress appetite, though typically not as severely as meth does.
Interestingly, cocaine binds to the protein structure of hair shafts, which is why hair testing can detect cocaine use for months after it occurs. This binding doesn't directly cause hair loss but indicates how drugs can interact with hair structures.
A 2021 study published in the Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment found that about 35% of regular cocaine users reported noticeable hair thinning, compared to 70% of meth users.
Key point: Cocaine affects hair through similar stress pathways as meth but typically causes less severe hair loss.
Opioids, including both prescription pain medications and illicit drugs like heroin, can affect hair growth through different mechanisms than stimulants, and individuals battling severe use often turn to a heroin rehab center for professional support.
These drugs can disrupt hormone production, particularly testosterone and estrogen, which play important roles in hair growth cycles. Research from the National Institute on Drug Abuse shows that opioid use can lower hormone levels by up to 40% in chronic users.
Opioid users may also experience nutritional deficiencies, though these typically stem from poor dietary choices rather than appetite suppression.
Key point: Opioid use can cause hair thinning primarily through hormonal disruption rather than the stress and malnutrition pathways seen with stimulants.
Benzodiazepines like Xanax (alprazolam) have less direct impact on hair than stimulants or opioids, though some individuals may still require benzodiazepine addiction treatment if dependence develops. These medications don't typically cause hair loss as a primary side effect.
However, if someone is taking Xanax for anxiety, the underlying anxiety condition itself might contribute to hair loss through stress pathways. In some cases, treating anxiety effectively may actually improve stress-related hair loss.
The relationship between benzodiazepines and hair health highlights how complex the connections between substances, mental health, and physical symptoms can be.
Key point: Benzodiazepines like Xanax have minimal direct effects on hair compared to stimulants, though underlying conditions being treated may impact hair health.

Recovery from meth-related hair loss is possible with the right approach, especially when it involves targeted stimulant addiction treatment. These strategies address the root causes of hair loss while supporting overall recovery.
Nutritional rehabilitation forms the foundation of hair recovery. The body needs proper building blocks to restart healthy hair growth. A balanced diet rich in these nutrients supports hair regrowth:
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, most people see improved hair growth within 3-6 months of correcting nutritional deficiencies. Supplements may help, but it's best to get nutrients from food when possible.
Gentle hair care practices also matter. Avoiding harsh chemical treatments, excessive heat styling, and tight hairstyles prevents further damage to fragile hair.
Proper hydration supports all cellular functions, including hair growth. The National Academy of Medicine recommends about 3.7 liters (125 ounces) of total water daily for men and 2.7 liters (91 ounces) for women.
Key point: Nutritional rehabilitation provides the building blocks needed for hair regrowth after meth use.
Reducing stress levels creates an environment where hair can regrow. Since stress hormones directly impact hair follicles, stress management becomes a crucial part of recovery. Evidence-based stress reduction techniques include:
Research from the American Psychological Association shows that consistent stress management can lower cortisol levels by up to 25% within 8 weeks. This reduction creates a more favorable environment for hair regrowth.
Many recovery programs incorporate these techniques as part of a holistic approach to healing from addiction. They address not only the psychological aspects of stress but also its physical manifestations.
Key point: Lowering stress hormone levels through consistent stress management practices creates conditions that support hair regrowth.
Professional addiction treatment addresses both the substance use disorder and its physical consequences, including hair loss. Comprehensive treatment programs typically include:
Many people with methamphetamine addiction also have co-occurring mental health conditions that require treatment, and resolving these issues may involve specialized addiction and depression treatment for sustained recovery. This dual diagnosis approach ensures that all factors contributing to substance use and physical symptoms are addressed.
At Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, CA, located in Marin County, CA, we offer integrated treatment that considers the whole person – not just the addiction, but all of its effects on physical and mental health. Our approach includes nutritional support and stress management techniques that can help with hair regrowth while addressing the underlying addiction.
Key point: Professional treatment addresses both the addiction and its physical consequences, creating the conditions needed for complete recovery.
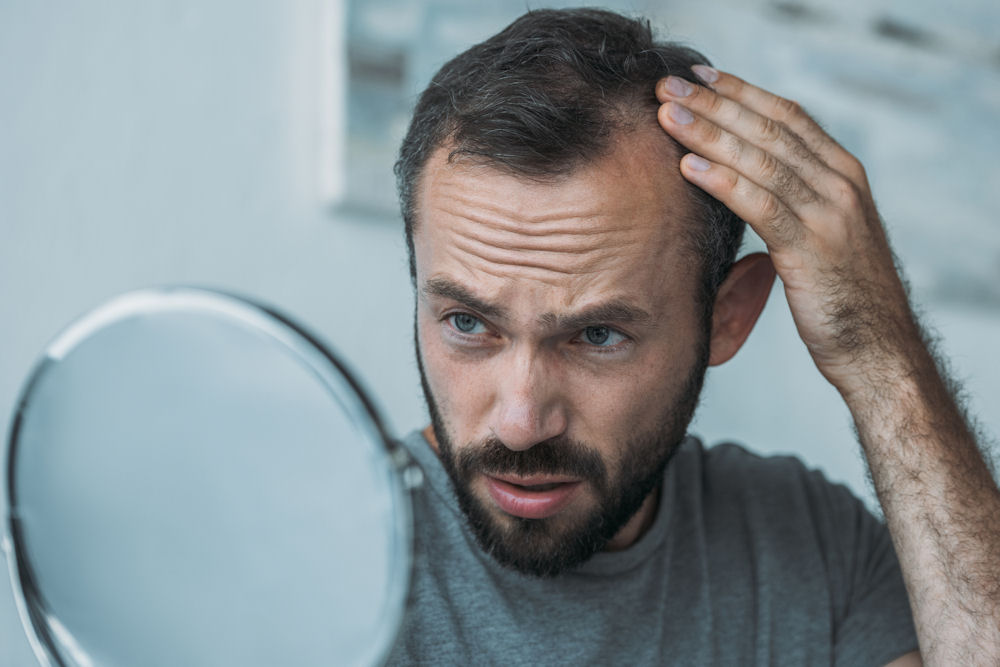

Recovery from methamphetamine addiction creates the conditions necessary for hair to regrow. When someone stops using meth, their body can begin healing in many ways.
During active addiction, the body directs its limited resources toward survival functions. Once in recovery, those resources can be redirected toward “non-essential” processes like hair growth. This shift doesn’t happen immediately, but gradually as overall health improves.
Improved nutrition plays a major role in this process. When someone in recovery begins eating regularly and nutritiously, their body receives the building blocks needed for hair growth. According to research from the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, nutritional improvements can stimulate new hair growth within 3-6 months.
Better sleep quality in recovery also supports hair health. During sleep, the body produces growth hormones and repairs tissues, including hair follicles. Studies show that people in recovery typically see sleep quality improve significantly within the first 90 days of sobriety.
The reduction in physical stress that comes with recovery further supports hair regrowth. Without the constant strain of meth use, the body’s stress response can normalize, reducing the levels of cortisol that can damage hair follicles.
Key point: Recovery creates multiple pathways for hair regrowth by improving nutrition, sleep, and stress levels.
Hair loss from methamphetamine use can be distressing, but it’s rarely permanent when addressed properly. The same steps that support recovery from addiction – improved nutrition, stress management, and professional treatment – also create the conditions for hair regrowth.
Recovery is a journey that includes physical healing alongside emotional and psychological growth. As the body recovers from the effects of meth, many physical symptoms improve, including hair loss. This process takes time and patience, but positive changes do occur with continued sobriety.
Many people find that visible improvements in their physical appearance, including hair regrowth, motivate them to maintain their recovery. These changes serve as tangible reminders of the body’s capacity to heal when given the chance.
For those concerned about hair loss related to methamphetamine use, a holistic rehab center offers the best path forward. By addressing the root causes of both the addiction and its physical effects, recovery becomes possible on all levels.
At Golden Gate Recovery, we understand the many ways methamphetamine affects the body, including hair loss. Our treatment programs address these physical effects alongside the psychological aspects of addiction, providing support for complete healing and recovery.
Hair loss may continue for several months after stopping meth use because the hair growth cycle takes 3-6 months to normalize. Nutritional deficiencies and stress effects also need time to resolve, even after drug use has ended.
In most cases, hair loss from meth use is not permanent if the drug use is stopped and proper nutrition and care are restored. However, extremely prolonged use or severe follicle damage may result in some permanent thinning.
Most people begin to see new hair growth within 3-6 months after stopping meth use and addressing nutritional deficiencies. Complete regrowth typically takes 12-18 months with proper nutrition and care.
Methamphetamine use can alter hair texture, making it brittle, dry, and prone to breakage due to nutritional deficiencies and dehydration. These changes are often reversible with recovery and proper hair care.
Meth-related hair loss typically affects the entire scalp rather than specific patterns, often accompanied by other symptoms like weight loss, dental issues, and skin problems. A healthcare provider can help determine the specific cause of your hair loss.
At Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, CA, we understand that the physical effects of methamphetamine addiction, including hair loss, can be distressing. Our comprehensive treatment programs address both the addiction itself and its physical consequences through evidence-based approaches and personalized care plans.
We believe in treating the whole person, not just the addiction, but all of its effects on physical and mental health. If you or someone you care about is struggling with methamphetamine use and its effects, we’re here to help. Contact Golden Gate Recovery today to learn more about our programs and how we can support your journey toward healing and recovery.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:
 Klonopin, a prescription medication widely used for its sedative effects, plays a critical role in managing anxiety and seizures. While it is generally well-tolerated when used as prescribed, Klonopin’s effects extend beyond its therapeutic benefits. One area of concern that often goes unnoticed is its impact on blood pressure. Many may ask, Does Klonopin lower blood pressure? The answer is yes, Klonopin can lower blood pressure, especially in individuals with pre-existing low blood pressure.
Klonopin, a prescription medication widely used for its sedative effects, plays a critical role in managing anxiety and seizures. While it is generally well-tolerated when used as prescribed, Klonopin’s effects extend beyond its therapeutic benefits. One area of concern that often goes unnoticed is its impact on blood pressure. Many may ask, Does Klonopin lower blood pressure? The answer is yes, Klonopin can lower blood pressure, especially in individuals with pre-existing low blood pressure.
Whether you’re using Klonopin for medical reasons or worried about its risks, understanding how it affects your cardiovascular system and blood pressure is key to protecting your health. At Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, California, we provide evidence-based outpatient treatment and behavioral therapy to help men recover from benzo addiction.
Klonopin, also known by its generic name clonazepam, is a benzodiazepine commonly prescribed to treat anxiety disorders, panic attacks, and seizure disorders. It works by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that helps calm excessive brain activity in the central nervous system. This action promotes relaxation, reduces anxiety, and helps prevent seizures. While Klonopin is effective for these conditions, its sedative properties also mean there’s a risk of addiction, and it should be used under careful medical supervision.
In addition to its calming effects, Klonopin can cause physical side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination. It may also impact cardiovascular functions, including heart rate and blood pressure, which can be especially concerning for individuals with pre-existing health conditions. Long-term use may affect vital signs and overall stability, making regular monitoring essential to minimize potential health risks.

As mentioned, Klonopin is primarily prescribed for the treatment of anxiety disorders, panic attacks, and seizure disorders. It is often used as a short-term solution for acute episodes of anxiety or as a long-term anxiety treatment option for individuals with chronic conditions. The drug works by stabilizing mood and reducing symptoms of excessive nervous system activity, such as racing thoughts or physical tremors associated with anxiety. For seizure disorders, Klonopin is often used as part of a broader treatment plan to prevent or reduce the frequency of seizures.
In addition to anxiety and seizures, Klonopin may also be prescribed for other conditions, including movement disorders and certain sleep-related issues. It is not typically a first-line treatment for most disorders, as it carries the potential for dependency and addiction. Healthcare providers usually recommend other therapeutic options before resorting to benzodiazepines like Klonopin, and it is often prescribed in combination with other therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for anxiety.
Klonopin can be addictive due to the way it interacts with the brain’s GABA receptors. As a central nervous system depressant, it provides a calming effect, leading users to feel more relaxed and less anxious. This feeling of relief can be highly reinforcing, causing individuals to want to take the drug repeatedly. Over time, the body builds a tolerance to the drug, meaning users must take larger doses to achieve the same calming effects, increasing the risk of addiction.
The addictive nature of Klonopin is compounded by its potential for withdrawal symptoms. When a person becomes physically dependent on the drug, stopping it abruptly can lead to symptoms like anxiety, irritability, and even more severe reactions like seizures. These withdrawal effects can make it difficult for individuals to stop using Klonopin, even if they want to, as the body has become reliant on the drug. Therefore, Klonopin is typically prescribed with caution, and any discontinuation should be done under medical supervision.
Klonopin abuse can lead to severe fluctuations in blood pressure, either lowering or raising it, depending on the circumstances. When abused, Klonopin may lead to an exaggerated calming effect that can cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to a drop in blood pressure. For individuals who misuse Klonopin by taking higher doses than prescribed, the risk of experiencing side effects such as dizziness and fainting becomes greater, as low blood pressure can cause reduced blood flow to vital organs.
Conversely, when individuals suddenly stop using Klonopin, withdrawal can trigger a surge in blood pressure. The body reacts to the absence of the drug by producing higher levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can increase heart rate and blood pressure. For those who have abused Klonopin for a long period, withdrawal can be especially difficult, and managing blood pressure during this time is crucial to prevent complications such as stroke or heart attack.

Klonopin’s effect on blood pressure can vary significantly in both the short-term and long-term. Understanding these effects is crucial for those taking Klonopin, especially when combined with other medications or in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
Klonopin induces relaxation and sedation, which can cause a temporary lowering of blood pressure. This is because the drug slows down the central nervous system, which can lead to a reduction in the body's overall stress response, resulting in lower heart rate and blood pressure in some individuals.
When you stand up quickly, you may experience a drop in blood pressure (known as orthostatic hypotension), which can cause dizziness or fainting. This is a typical side effect of Klonopin and other benzodiazepines, particularly when starting the medication or increasing the dosage.
The relaxing effects of Klonopin can also slow down the heart rate. This may cause a temporary drop in blood pressure, particularly in those who already have low blood pressure. In some cases, this reduction in heart rate can make individuals feel lightheaded or fatigued, especially during physical activity or sudden movements.
Over time, your body may develop tolerance to Klonopin, which can reduce the sedative effects. As tolerance develops, the drug's ability to lower blood pressure may diminish, and blood pressure may return to baseline or even increase, especially if the drug is used with other substances that affect the cardiovascular system.
Long-term use of Klonopin can lead to physical dependence. Abrupt withdrawal or a significant decrease in dosage can cause rebound anxiety or an increase in blood pressure, as the body may react to the sudden change in medication levels.
Chronic use of Klonopin may have indirect effects on circulation and blood pressure regulation. For some individuals, this may exacerbate existing cardiovascular issues or contribute to irregularities in blood pressure regulation, particularly when used in conjunction with other medications that affect the heart or blood pressure.
For many individuals, Klonopin can lower blood pressure, especially during the initial stages of treatment. This effect is part of the drug’s calming properties, which can lead to drowsiness, dizziness, and a feeling of lightheadedness. These symptoms can be dangerous, particularly for individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or those who are prone to fainting.
While lowered blood pressure can help manage anxiety, it poses risks when it becomes too low. Hypotension, or excessively low blood pressure, can lead to dizziness, fainting, and falls, which can be particularly dangerous for older adults or those with mobility issues. Chronic low blood pressure may also strain the heart and organs over time.
On the other hand, in some instances, Klonopin can cause elevated blood pressure, particularly when abused or during withdrawal. As the body reacts to the lack of the drug, anxiety levels rise, which can lead to an increase in blood pressure. This is especially true for individuals who have been using Klonopin regularly and suddenly stop, triggering a rebound effect.
Elevated blood pressure puts additional stress on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. In severe cases, uncontrolled hypertension can lead to life-threatening events. Managing blood pressure during and after Klonopin withdrawal is crucial to prevent long-term health complications.

If you or someone you love is struggling with Klonopin addiction, seeking professional help is the first step towards recovery. At Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, CA, we offer specialized treatment programs designed to help individuals safely manage withdrawal symptoms, including blood pressure fluctuations, while recovering from Klonopin addiction.
With the right support and medical supervision, you can regain control of your health and well-being. Contact us now!
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Gabapentin misuse is becoming more common, especially when combined with other substances. While it’s not classified as a controlled substance federally, it still carries risks. Misuse can lead to dependence, withdrawal symptoms, and other health complications. Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, California, provides evidence-based treatment for individuals struggling with gabapentin misuse and co-occurring mental health conditions. If you or someone you know needs help, contact us to explore treatment options and take the first step forward.
Gabapentin is a prescription medication used to treat nerve pain, seizures, and sometimes restless leg syndrome. Doctors often prescribe it when other options fail to provide adequate results. Gabapentin works by calming overactive nerve signals in the brain, thereby helping to reduce symptoms associated with nerve-related disorders. It is not classified as an opioid or benzodiazepine and belongs to a different class of medications called gabapentinoids.
In addition to its approved uses, gabapentin is sometimes prescribed off-label for conditions such as anxiety disorder, insomnia, and migraines. For those seeking anxiety treatment in Marin County, gabapentin may be part of a supervised care plan, though it still requires careful medical oversight. Some individuals report feeling relaxed or slightly euphoric after taking gabapentin, which can contribute to its misuse. The medication is typically available in capsule or tablet form and is taken orally, often multiple times a day. Dosage depends on the condition being treated and individual tolerance.
Gabapentin may be used short-term or long-term, depending on the patient’s needs. Like with any prescription medication, following medical instructions is essential. Even though it is legal with a prescription, gabapentin can still be misused, especially when used outside the prescribed dosage or for nonmedical purposes.

Although gabapentin is not listed as a controlled substance under federal law, several states have placed restrictions on it due to increasing concerns about misuse. Misuse can occur when the drug is taken in larger amounts, more frequently than prescribed, or in combination with other substances to achieve psychoactive effects. The drug can produce sensations of relaxation, calmness, or mild euphoria in some individuals, particularly at high doses.
Over time, tolerance to gabapentin can develop, meaning that users may need higher doses to achieve the same effects. This increase in dosage raises the risk of developing physical dependence. Individuals who take gabapentin regularly and then stop abruptly may experience withdrawal symptoms, which are a sign of physiological adaptation.
While gabapentin is not considered as addictive as opioids or benzodiazepines, it still presents risks, especially when used improperly. Research shows a growing trend in gabapentin misuse, often among people who use it alongside other substances such as opioids or alcohol. These combinations increase the likelihood of adverse outcomes, including sedation and respiratory depression.
Medical professionals are now more cautious in prescribing gabapentin, especially in high-risk populations. Using gabapentin strictly according to prescription guidelines helps reduce the potential for misuse and associated health risks.
Gabapentin misuse occurs when the drug is taken in a manner not intended by the prescriber. This includes taking larger doses, using it without a prescription, or combining it with other substances to intensify its effects. Misuse can lead to physical dependence, impaired functioning, and various health complications.
Common indicators of gabapentin misuse include:
These behaviors may develop gradually. While some signs may resemble side effects, patterns of misuse often become more noticeable over time. When misuse is suspected, early intervention can prevent further complications. A professional assessment can determine whether addiction treatment is necessary and what options are appropriate for the individual’s situation.

Yes, individuals who use gabapentin for extended periods, especially at high doses, may experience withdrawal symptoms if they stop suddenly. These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the dosage, length of use, and individual health factors. Withdrawal suggests the body has become physically dependent on the drug.
The risk of withdrawal is higher when gabapentin is stopped abruptly. Medical guidelines usually advise reducing the dose slowly under supervision to help the body adapt. For individuals who have developed a significant dependence, withdrawal management may be part of a structured treatment plan. Though withdrawal from gabapentin is rarely life-threatening, it can be distressing and may lead some individuals to resume use to relieve symptoms.
Withdrawal itself does not confirm addiction but suggests the presence of physical dependence. In some cases, dependence can progress to addiction, particularly if gabapentin is misused repeatedly or taken with other substances.
Treatment for gabapentin misuse involves a combination of medical oversight, behavioral therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. The first step is usually a comprehensive medical and psychological evaluation to determine the extent of use and any co-occurring mental health conditions. If physical dependence is present, supervised detox may be necessary. This often involves a gradual reduction in dosage to manage withdrawal symptoms and avoid complications like seizures.
Behavioral therapies, especially cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), are widely used in treatment. CBT helps individuals recognize and modify patterns of thinking and behavior that contribute to misuse. In addition to individual counseling, group therapy and peer support may also be part of a recovery plan. These settings provide accountability and structure during the treatment process.
Many individuals who misuse gabapentin may also misuse other drugs. In these cases, treatment plans must address multiple substances. Integrated care ensures all factors influencing substance use are considered. Some individuals benefit from residential treatment programs, while others do well with outpatient care, depending on the severity of their condition and their support systems.
Relapse prevention strategies are typically incorporated into treatment to help individuals manage triggers, cravings, and high-risk situations. Developing coping skills and creating a structured daily routine can also contribute to long-term stability. The goal is to reduce reliance on medication for nonmedical reasons and improve overall functioning.

Golden Gate Recovery offers services for individuals with both substance misuse and co-occurring mental health conditions. This type of care, called dual diagnosis treatment, is essential for people who misuse gabapentin and also experience mental health challenges such as anxiety, depression, or mood disorders. Addressing both issues at the same time helps reduce relapse rates and improve treatment outcomes.
Each client receives a personalized treatment plan based on their specific clinical needs. A team of professionals works together to address both the psychological and behavioral aspects of substance misuse. Therapy sessions may include evidence-based approaches like CBT and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), as well as life skills training and relapse prevention.
Medication management is available for individuals who need psychiatric stabilization. The focus is on using medications appropriately while minimizing the risk of further misuse. Clients are also introduced to practical tools for managing stress, regulating emotions, and improving daily routines.
Group therapy is often part of treatment to encourage connection and promote accountability. Education on substance use, mental health, and recovery strategies is part of the program. Golden Gate Recovery emphasizes practical outcomes by helping individuals build stability in multiple areas of life, including relationships, work, and health. Their program aims to support long-term behavioral change through consistent, evidence-informed care.
Yes, drowsiness is a common side effect. It can impair driving, operating machinery, or performing tasks requiring attention.
Some users report weight gain, though it varies by individual. It may be related to increased appetite or reduced activity levels.
No, stopping suddenly can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Tapering the dose under medical supervision is recommended.
No. Combining gabapentin with alcohol can increase sedation and may lead to respiratory depression or overdose.
Gabapentin typically stays in the body for one to two days, depending on factors like dosage and metabolism.
No. Gabapentin is a gabapentinoid used for nerve pain and seizures. Xanax is a benzodiazepine used for anxiety.
Yes. Misuse and dependence can occur even with a prescription, especially when directions are not followed closely.

Individuals struggling with gabapentin misuse can access treatment services across California. Many programs provide detox support, therapy, and relapse prevention tools to address both the physical and behavioral components of substance misuse. A professional assessment can help determine the right type of treatment—whether outpatient, inpatient, or medically supervised detox.
Golden Gate Recovery offers structured treatment for individuals with prescription drug misuse, including cases involving gabapentin. Their programs address both substance use and co-occurring mental health concerns, using evidence-based practices and tailored treatment plans. Services include counseling, therapy, and recovery planning focused on functional improvement and sustained recovery.
Seeking help early can prevent long-term complications associated with misuse. While outcomes vary, most individuals benefit from a combination of medical supervision and behavioral intervention. For those unsure where to begin, speaking with a treatment provider is a practical first step. Contact us today to learn more about your options and take the first step toward recovery.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

If you or a loved one is struggling with sleep, Ambien may seem like a miracle drug—but understanding Ambien side effects is crucial to avoid serious health risks and dependency. While this popular sleep aid can be effective in the short term, long-term use carries a host of side effects and the potential for addiction. Misuse of Ambien (zolpidem) can quickly spiral into a prescription drug dependency, often masked under the guise of trying to get a good night’s sleep.
At Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, California, we understand the delicate balance between managing sleep disorders and avoiding harmful dependence on prescription drugs.
Our guide provides valuable information on what Ambien is, how it affects the brain and body, the signs of misuse, and how Golden Gate Recovery’s specialized prescription drug addiction treatment program in Marin County, California, can help you or a loved one promote recovery.
Ambien (generic name: zolpidem) is a prescription sedative-hypnotic medication commonly used to treat insomnia, particularly for people who have trouble falling asleep. It works by enhancing the effects of GABA, a neurotransmitter in the brain that promotes relaxation and sleep.
Doctors typically prescribe Ambien for short-term use, usually no longer than two to four weeks. Despite this, many individuals continue to rely on Ambien for months or even years—greatly increasing their risk of developing a tolerance, dependency, or full-blown addiction.

Like all medications, Ambien comes with side effects. Understanding these effects can help users recognize when the risks begin to outweigh the benefits.
Some of the more frequently reported side effects include
While these Ambien side effects are typically temporary, persistent symptoms should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
When used over an extended period or misused, Ambien can cause more serious complications, including:
Ambien can cause unusual behaviors during sleep, such as sleepwalking, sleep-driving, cooking, eating, or even making phone calls—all while the person is not fully conscious. These actions often occur without any memory of the event, posing serious safety risks to the individual and others.
Long-term use of Ambien has been linked to negative changes in mood. Users may experience heightened anxiety, irritability, or even depressive symptoms. In some cases, preexisting mental health conditions can worsen, and individuals may feel emotionally unstable or detached.
Extended use of Ambien can impair cognitive function. People may have trouble concentrating, experience delayed reaction times, or notice memory issues. These cognitive deficits can interfere with daily tasks, work performance, and overall quality of life.
When Ambien use is stopped, especially abruptly, individuals often experience rebound insomnia—a temporary worsening of sleep problems. This can include difficulty falling asleep, frequent waking during the night, and poorer sleep quality than before starting the medication.
With continued use, the body can develop a tolerance to Ambien, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect. This increases the risk of physical and psychological dependence, where stopping the drug can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, tremors, nausea, and sleep disturbances. Professional medical support is often necessary for safe and effective discontinuation.
Understanding the potential risks associated with Ambien—particularly when used beyond short-term treatment—can empower individuals to seek safer, sustainable solutions for sleep issues.

Yes. Ambien is often mistakenly thought to be “safe” because a doctor prescribes it, but it has a high potential for addiction, mainly when used outside prescribed guidelines or in combination with other substances.
Ambien addiction can be psychological, physical, or both. Users may feel they cannot fall asleep without the drug, leading to compulsive use. Over time, they may escalate doses, hide usage from loved ones, or continue use despite harmful consequences.
Some key signs of Ambien addiction include:
Mixing Ambien with alcohol, opioids, or benzodiazepines can be extremely dangerous, and in some cases, even fatal. All of these substances depress the central nervous system, and when taken together, they can intensify one another’s effects. This interaction can result in severe sedation, slowed or stopped breathing, blackouts, overdose, coma, or even death.
Even without the intent to misuse, someone may take Ambien and have a glass of wine, unknowingly putting themselves at significant risk. The combination of sedatives dramatically increases the likelihood of memory lapses, accidental injuries, and life-threatening complications. For these reasons, it’s critical to avoid mixing Ambien with any other depressants unless specifically directed by a healthcare professional.

Recognizing the signs of Ambien misuse is the first step toward healing. If you or someone you know is showing the following symptoms, it may be time to seek professional help:
Often, Ambien misuse is accompanied by other mental health challenges, such as depression, anxiety, or trauma. That’s why a comprehensive treatment approach is essential.
At Golden Gate Recovery, we offer compassionate, personalized treatment for those struggling with Ambien (zolpidem) addiction. Our approach addresses both the physical dependence and the emotional and psychological factors behind prescription drug use, combining evidence-based therapies with holistic care to support lasting recovery.
Our medical team ensures a safe and closely monitored drug and alcohol detox process to manage Ambien withdrawal symptoms and stabilize clients before entering deeper therapeutic work.
Through addiction counseling, we address the underlying reasons behind Ambien misuse, such as trauma, chronic insomnia, anxiety, or stress—common drivers of prescription drug addiction.
To sustain long-term recovery, we provide customized aftercare plans, including ongoing therapy, relapse prevention strategies, peer support, and lifestyle adjustments to build a healthy, medication-free future.
Stopping Ambien abruptly can cause withdrawal symptoms or rebound insomnia. If you’ve been using Ambien regularly or in high doses, it’s important to:
If Ambien use has become problematic, professional treatment can help. At Golden Gate Recovery, we offer medical detox, counseling, and relapse prevention to support individuals safely stopping Ambien and building long-term recovery.

Understanding Ambien side effects and risks of dependency is the first step in protecting your health and well-being. What starts as a seemingly harmless sleep aid can turn into a life-altering addiction—but there is hope. Golden Gate Recovery in Marin County, CA, is here to help. Our compassionate team is here to support you throughout detoxification, treatment, and long-term recovery. Contact us now!
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:

Benzodiazepines (benzos) can remain in the body for varying durations depending on the specific type, dosage, frequency of use, and individual metabolism. Short-acting benzos like Xanax may be detectable for a few days, while long-acting ones like Valium can linger for over a week.
Detection windows also vary by test type—urine tests typically detect benzos for 1–7 days, while hair tests may show use for up to 90 days. For individuals navigating recovery, understanding these timelines is key. Learn more about holistic, evidence-based support at Golden Gate Recovery, where personalized care fosters long-term healing.
Benzodiazepines are a class of prescription medications commonly used to treat anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and muscle spasms. They work by enhancing the effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that calms brain activity. While effective short term, benzos carry a high risk of dependence and withdrawal symptoms with prolonged use.
Common benzodiazepines include:
Proper use and monitoring are essential to avoid misuse and addiction.
Benzodiazepines act on the central nervous system by enhancing the effects of GABA, a neurotransmitter that inhibits brain activity. This results in sedation, reduced anxiety, and muscle relaxation. While effective for short-term relief of panic, insomnia, and seizures, long-term use can lead to tolerance, dependence, and cognitive impairment. Understanding these effects helps guide safe use and treatment planning.
| Effect | Brain Impact | Body Impact |
| Sedation | Slows neural activity | Causes drowsiness and fatigue |
| Anxiety reduction | Calms overactive brain signals | Lowers heart rate and blood pressure |
| Muscle relaxation | Reduces motor neuron excitability | Eases muscle tension and spasms |
| Memory impairment (long-term) | Disrupts short-term memory processing | May affect coordination and alertness |
| Dependence risk | Alters reward and tolerance pathways | Withdrawal symptoms upon cessation |
A drug’s half-life refers to the time required for its concentration in the body to decrease by 50%. Several factors influence this rate, affecting how long a drug remains active and how frequently it must be administered. Liver and kidney function are critical, as these organs metabolize and eliminate drugs. Age, body composition, and genetic differences also play roles in drug processing. Additionally, dosage levels, drug interactions, and the route of administration can alter absorption and clearance. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing treatment plans, minimizing side effects, and ensuring therapeutic effectiveness across diverse patient populations.
| Factor | Description |
| Age | Older adults may have slower metabolism and reduced organ function. |
| Liver Function | An impaired liver reduces drug metabolism, prolonging half-life. |
| Kidney Function | Poor renal clearance delays drug elimination. |
| Body Composition | Fat-soluble drugs may accumulate in adipose tissue, extending half-life. |
| Drug Dosage | Higher doses may saturate metabolic pathways, altering the elimination rate. |
| Drug Interactions | Other medications can inhibit or enhance metabolism and clearance. |
| Genetics | Genetic variations affect enzyme activity and drug metabolism. |
| Route of Administration | IV drugs may have shorter half-lives than oral forms due to absorption rates. |
Drug clearance refers to the body's ability to eliminate a substance through metabolic and excretory processes, primarily via the liver and kidneys. It is a key determinant of a drug’s half-life and influences dosing frequency and therapeutic levels. Efficient clearance ensures that drugs do not accumulate to toxic levels.
Factors affecting clearance include age, organ function, genetics, and drug interactions. Impaired liver or kidney function can slow clearance, requiring dose adjustments to maintain safety and efficacy in treatment.
The volume of distribution (Vd) describes how extensively a drug disperses throughout body tissues relative to the bloodstream. A high Vd indicates that the drug is widely distributed into tissues, while a low Vd suggests it remains largely in the plasma. This metric helps determine appropriate dosing.
Factors influencing Vd include lipid solubility, protein binding, and body composition. Lipophilic drugs tend to have higher Vd due to accumulation in fat stores, affecting both drug duration and elimination rates.
Patient-specific variables significantly impact drug response, metabolism, and safety. Age, weight, sex, and genetic makeup influence how a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted. For example, older adults may have reduced liver or kidney function, altering drug clearance.
Other factors include comorbid conditions, concurrent medications, and lifestyle habits such as diet or smoking. These variables can lead to drug interactions or altered therapeutic effects, making personalized dosing and careful monitoring essential for safe and effective treatment.

Benzodiazepine addiction is a growing concern, especially among individuals prescribed these medications for anxiety, insomnia, or seizures. While effective short-term, long-term use can lead to dependence, misuse, and serious health risks. Understanding the causes, recognizing the signs, and ensuring accurate diagnosis are essential for early intervention and effective treatment. This overview outlines the key factors that contribute to benzo addiction, the behavioral and physical indicators of misuse, and the clinical tools used to assess and diagnose the condition.
Benzodiazepine Use Disorder involves compulsive use despite harm, often stemming from long-term or misuse of prescriptions for anxiety or insomnia. It leads to tolerance, dependence, withdrawal, and impaired functioning. Diagnosis follows DSM-5 criteria, assessing behavior, physical symptoms, and psychological effects.
Benzo withdrawal occurs when use is reduced or stopped after dependence develops. Symptoms range from mild (anxiety, insomnia, irritability) to severe (tremors, panic attacks, seizures), often appearing within hours to days. Severity varies by dosage, duration, and health, making medical supervision crucial at our medical detox center in Marin County, California, for safe detox and symptom management.
| Symptom Category | Examples |
| Psychological | Anxiety, panic attacks, irritability, depression |
| Neurological | Tremors, confusion, headaches, seizures |
| Sleep-related | Insomnia, nightmares, restlessness |
| Physical | Muscle pain, sweating, nausea, heart palpitations |
| Cognitive | Poor concentration, memory issues |
The length of time benzodiazepines stay in the body depends on the specific drug, dosage, frequency of use, and individual factors such as age, metabolism, and organ function. Short-acting benzos like alprazolam may clear within a day, while long-acting types like diazepam can remain detectable for several days or even weeks. Benzos are typically metabolized in the liver and excreted through urine. Drug tests can detect them in urine, blood, saliva, or hair for varying durations. Chronic use may extend detection windows, making it important to consider both pharmacological and personal variables when assessing clearance.
| Test Type | Short-Acting Benzos | Long-Acting Benzos |
| Urine | 1–3 days | 7–10+ days |
| Blood | 6–24 hours | 1–3 days |
| Saliva | Up to 2 days | Up to 5 days |
| Hair | Up to 90 days | Up to 90 days |
Benzodiazepine addiction treatment involves a structured, medically supervised approach to safely manage withdrawal and support long-term recovery. Gradual tapering is essential to reduce withdrawal risks, often combined with behavioral therapies and holistic care. Treatment may occur in inpatient, outpatient, or residential settings depending on severity. Addressing co-occurring mental health conditions enhances outcomes, while peer support and relapse prevention strategies help sustain progress.

Recovering from drug addiction at Golden Gate means receiving compassionate, evidence-based care tailored to your unique journey. Our holistic approach addresses both physical dependence and underlying emotional challenges, helping you build lasting resilience and clarity.
Our experienced clinical team includes licensed therapists, addiction specialists, and peer support professionals who guide you through every stage of recovery. From detox to aftercare, we prioritize connection, empowerment, and long-term healing.
If you or a loved one is ready to take the first step toward recovery, contact us today. We’re here to listen, support, and help you reclaim a life free from addiction.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:
Is cocaine a stimulant or depressant? The DEA answers that this illicit drug is a stimulant. Yet, this stimulant also has depressive effects, which we’ll learn later. Most importantly, what makes it so harmfully addictive? Here, we not only answer the debate of stimulant vs depressant, but also the important question of how you can recover from cocaine addiction.
At Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, California, located in Marin County, we provide men with the tools and resources they need to recover from cocaine addiction. Without further ado, here are all the details surrounding cocaine’s effects and why it’s so harmful to the human body.

Cocaine is an extremely addictive substance derived from the leaves of the coca plant, which is native to South America. It is primarily found as an illicit drug that some individuals consume to experience euphoria. In rare instances, it is also utilized as a prescribed medication for anesthesia in specific surgical procedures.
As an illegal street drug, cocaine typically appears as a fine, white, crystalline powder. Street vendors occasionally adulterate it with cornstarch, talcum powder, or flour to increase its apparent volume, thereby maximizing their profits. They may also combine it with other illicit substances. Another variant of this drug is crack cocaine, which is produced by heating cocaine to form a rock-like crystal.
Cocaine is a very powerful stimulant that accelerates central nervous system function to abnormal degrees. The drug stimulates dopamine release in the brain, resulting in excessive feelings of euphoria. However, these CNS and dopamine stimulations are the reason for its physical harm. These aforementioned impacts result in high strain on your vital organs, including the cardiovascular system.
Cocaine abuse and addiction have very tell-tale characteristics if you know what to look for. Seek the appropriate professionals if you notice any of these behavioral or visual indicators.
The indicators of cocaine abuse can differ significantly among individuals, influenced by factors such as the quantity of cocaine consumed and the duration of use. Some examples of symptoms that may manifest in a person abusing cocaine include:
Signs of cocaine abuse include the following:
The most visual indication is perhaps severe redness or bloodshot eyes. This redness will often be prominent in cocaine addiction sufferers, regardless of whether or not they are currently under the influence.
Cocaine has accelerated effects on the central nervous system and cardiovascular functions. This result is uncontrollable and irrepressibly high energy levels. They will exhibit this through rapid, unnatural movements and behaviors to include working at an unusually high rate. Take notice of anybody exhibiting overanxious energy levels that look out of place.
In correlation with abnormally high energy levels comes rapid speech. This is a common side effect of cocaine use and abuse that the user is unaware of. They may think they are speaking normally, but their speech will come across as rapid to indiscernible levels. If you observe any unusual behaviors of rapid, indiscernible speech, get them the help they need today.
A cocaine addiction is a very expensive habit. Consequently, the addicted party may indulge in addiction-provoking behaviors to feed that habit, such as stealing money or possessions. This occurs when the mind and body have reached a level of dependency that causes them to become desperate to feed their fix. This addiction-fueled mentality often leads to resorting to stealing to feed their habit at any cost, regardless of the consequences.
The term “cocaine eyes” refers to the heavy dilation of pupils that occurs as a result of cocaine abuse. This is a very evident symptom, as cocaine’s dilation of pupils has the opposite effect that other drugs have. These large pupils are a tell-tale sign and should be met with swift action. Seek the appropriate authorities at your discretion if you observe this or the other aforementioned symptoms on this list.

The greatest way to get the motivation and confidence to seek addiction treatment is to understand cocaine’s negative bodily effects. Here is a brief rundown of the many mind and body strains that lead to permanent health defects in the long run.
Regarded as the most potent substance derived from natural sources, cocaine is available in both powdered and crystallized rock forms, and can be consumed through smoking, injection, or inhalation.
When individuals use cocaine, they undergo a high that induces profound feelings of euphoria and excitement by enhancing the release of dopamine in the brain while simultaneously inhibiting the brain’s pain receptors. Excessive use of cocaine leads to alterations in the brain’s reward system, which ultimately results in tolerance, addiction, and dependence.
Recognized as an exceptionally addictive substance, those who use cocaine frequently struggle to cease their usage. These individuals may begin to face disruptions in various aspects of their lives and their relationships. However, with appropriate intervention, effective treatment can be achieved, allowing individuals to regain a sober lifestyle.
Cocaine’s chemical compounds block neurotransmitters that regulate dopamine levels. As a result, your body releases abnormal levels of dopamine, “feel good” cells into your bloodstream. These feelings of euphoria are very short-lived, causing a severe crash after the fact. In other words, after the initial rush of dopamine, your body goes through a “crash” recovery period in an attempt to restore natural neurobiological frequencies.
As alluded to at the end of the previous section, your body undergoes a severe crash after the initial euphoric rush. This means your body goes into a severe mental and physical depressive state to restore your body’s natural chemical levels. As a result, you will feel severe fatigue, lethargy, and even sadness as your body undergoes this difficult recovery period.
Your brain is heavily affected by the presence of cocaine because it is considered a foreign agent to the body. Once your mind is exposed to cocaine’s chemical compounds, it feeds off the dopamine rush and adapts to cocaine’s alterations. In short, your mind makes room for this compound by neurologically requiring trace amounts of the drug to function normally. This is when dependency forms as your mind develops a dependency or craving for this drug. Without which, you will begin to experience very uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms.
Once dependency is developed, your mind and body acquire severe withdrawal symptoms. Therefore, you will begin to experience severe pain and discomfort throughout your body until your next dose. Only when your dose is satisfied do these withdrawals subside momentarily. This causes a dangerous and repetitive loop of substance abuse that is only recoverable with professional addiction treatment.
Cocaine’s euphoric sensations don’t come without severe mental health consequences. Unbeknownst to many, cocaine is the cause of many mental health conditions, some of which are irreparable. Below is a brief overview of cocaine’s effects on mental health.
This goes in direct correlation with cocaine’s fine line between euphoria and despair. That is to say, cocaine’s overstimulation of dopamine incurs serious mental health consequences through induced depression. When the body is perpetually exposed to overstimulated dopamine levels, the body often develops severe deficiencies leading to depression. Fortunately, you can restore some degree of neurochemical stabilization by seeking professional detox programs. Once your body expels this dependency from your body, your mental well-being begins the restoration process.
Dopamine is not the only chemical affected by cocaine use. Neuropathways and other neurobiological frequencies are severely affected, causing drastic mood swings, fatigue, and other mental deficiencies. These effects stem from cocaine’s interference with proper neurotransmitter communication. This results in misfiring neurons, which can induce permanent mental defects with prolonged cocaine use.
After the effects of cocaine wear off, the cocaine crash has adverse effects on anxiety levels. That’s because dopamine, which is also responsible for regulating mood and anxiety, is severely destabilized after the fact. This contributes to elevated anxiety in the absence of dopamine as your body attempts to replenish the dopamine lost during cocaine use.
All of the factors mentioned previously are direct contributors to inducing several types of mental health problems. The elevated anxiety levels, destabilized frequencies, and dopamine deprivations associated with cocaine crashes are directly linked to personality, depression, and anxiety disorders. If the depth of your addiction is severe enough, these mental health conditions may even be irreversible. However, stopping now prevents further mental health harm from being done while minimizing mental health condition symptoms.
This symptom’s literal definition is an utter inability to feel pleasure, regardless of how enjoyable the activity is. This occurs when your body has been so severely overstimulated that it induces a dangerous trenching of pleasure cells. As a result, this torturous feeling renders your mental capacity incapable of feeling pleasure. If this symptom describes you, it is especially crucial to immediately consult a treatment specialist.
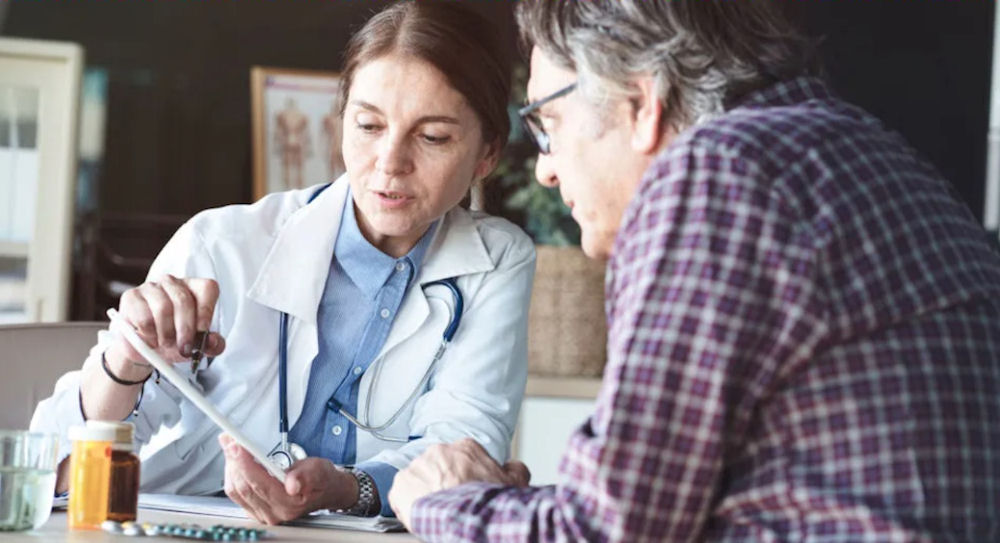

Though cocaine is classified as a stimulant, the associated crash inflicts depressant effects during the attempted restoration process. Here are the contrary depressive effects this stimulant has on the body after initial use.

If you or someone you care about is struggling with cocaine addiction or another substance use disorder, it is not too late to pursue treatment. At Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, CA, we will assist you in navigating each stage of treatment and the services available at each facility.
Treatment for cocaine addiction may involve a mix of inpatient care, behavioral therapies, and additional options. The cocaine treatment programs we provide at our men’s rehab center may consist of:
Individuals who enter outpatient treatmentbenefit from the ability to live at home with the stability of a flexible schedule while still receiving the treatment needed to stay on the path to recovery.
In this setting, clients are afforded more independence compared to residential treatment programs. Partial hospitalization programs may be suitable for patients who are highly motivated to recover and/or have completed more intensive treatment options.
Intensive outpatient programs are structured so that patients attend a facility for treatment during the day and return home or to a sober living environment in the evening. This option is appropriate for patients who have shown they do not require 24-hour supervision.
Following the completion of an inpatient or outpatient program, many individuals find it beneficial to reside in a sober living environment, supported by peers and staff who offer medical services, job opportunities, and other resources as they reintegrate.
Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, California, is your lifeline to a happier life in sobriety. We exhibit these joys through our enjoyable rehab programs and treatment procedures. You don’t have to suffer the impact of addiction or withdrawals thanks to our cutting-edge symptom-alleviating therapy. Expose yourself to the fullness of life’s joys and opportunities apart from addiction by contacting us today.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:
 Muscle relaxers are often a go-to solution for people struggling with pain and muscle spasms, offering quick relief and making it easier to get through the day. These medications can seem like a lifeline for those with chronic back pain, a sports injury, or general muscle tension. But here’s the question many don’t think to ask: Are muscle relaxers addictive? What starts as a temporary fix for pain can gradually become a daily necessity, and before you know it, you’re depending on them more than you intended.
It’s crucial to recognize the signs of drug addiction and the prescription drug treatment options available to help you break free from this dangerous cycle. At Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, California, we provide men with the tools and resources to combat an addiction to muscle relaxers.
Muscle relaxers are often a go-to solution for people struggling with pain and muscle spasms, offering quick relief and making it easier to get through the day. These medications can seem like a lifeline for those with chronic back pain, a sports injury, or general muscle tension. But here’s the question many don’t think to ask: Are muscle relaxers addictive? What starts as a temporary fix for pain can gradually become a daily necessity, and before you know it, you’re depending on them more than you intended.
It’s crucial to recognize the signs of drug addiction and the prescription drug treatment options available to help you break free from this dangerous cycle. At Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, California, we provide men with the tools and resources to combat an addiction to muscle relaxers. 
Muscle relaxers, also known as muscle relaxants, are prescription medications aimed at improving muscle function and alleviating symptoms like muscle spasms and discomfort caused by injuries, inflammation, or neurological disorders. They primarily operate as central nervous system depressants, inducing sedation or inhibiting pain signal transmission from the nerves to the brain.
Muscle relaxants are split into two categories: antispasmodics, which target smooth muscles or the CNS to alleviate muscle spasms, and antispastics, which address spasticity by reducing nerve signals responsible for muscle contractions. Antispastics are particularly effective for conditions such as strokes, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries, and cerebral palsy. Antispasmodics are medications that alleviate muscle spasms, especially within the digestive system.
While both types serve distinct purposes within muscle function management, some medications like diazepam are also prescribed for non-muscle-related issues, highlighting the versatility of these medications in clinical practice.
Antispasmodics are drugs designed to alleviate muscle spasms, especially in the skeletal muscles associated with the digestive system and urinary tract. These muscle relaxants typically function by acting on the central nervous system to diminish the nerve signals that trigger muscle contractions. They specifically target the smooth muscles lining these organs to alleviate muscle tension, spasms, contractions, cramps, and associated pain.
Antispasmodics are commonly employed to address issues such as abdominal cramping, bloating, and discomfort linked to irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). They also help decrease the frequency and urgency of urination in individuals suffering from an overactive bladder and provide relief from pain and discomfort related to urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Although antispasmodics have the potential for addiction, particularly when misused or taken in conjunction with other substances, the level of risk varies based on the specific medication and individual circumstances. Some antispasmodics, similar to certain muscle relaxants, present a moderate to low risk of addiction, while others, especially those prescribed for severe pain or individuals with a history of substance abuse, may pose a higher risk. It is essential to consult your healthcare provider for guidance.
Antispastic muscle relaxants are prescribed to manage spasticity, characterized by abnormal muscle movement patterns or simultaneous contractions due to nerve pathway damage in the spinal cord or skeletal muscles that regulate movement and stretch reflexes. These medications improve muscle tightness (hypertonicity) and involuntary spasms by acting on the central nervous system, particularly the spinal cord or skeletal muscle.
In contrast to centrally acting muscle relaxants, direct-acting muscle relaxants target muscle tissue directly. Antispastic drugs such as Baclofen and Dantrolene (Dantrium) are regarded as the primary treatment option for chronic spasticity, particularly in adults with spinal cord injuries and neurological conditions such as Cerebral palsy (CP) and multiple sclerosis (MS).
These medications block the signals that trigger muscle contractions at the root of the muscle fibers, allowing muscles to relax to alleviate spasms and stiffness. While effective, muscle relaxers are generally prescribed for short-term use and have a risk of dependency and addiction when taken for prolonged periods, especially when misused.
Like all medications, muscle relaxers can cause side effects, especially when used improperly or for prolonged periods. Some of the common side effects of muscle relaxants include
While these side effects may subside with time, they can also become more problematic when muscle relaxers are misused or abused. Prolonged use can lead to increased tolerance and physical dependence.

Muscle relaxers can be addictive, particularly when they are used outside of their prescribed purpose. The potential for addiction increases when individuals misuse muscle relaxers by taking them in higher doses than prescribed, using them without a prescription, or combining them with other substances like alcohol or opioids.
Certain muscle relaxers, such as carisoprodol (Soma), are more likely to lead to dependence due to their sedative properties. When these medications are abused, they can induce a feeling of euphoria or relaxation, which makes them desirable for individuals looking to escape stress or physical discomfort. As time passes, the body may build a tolerance to the drug, requiring individuals to take larger doses to experience the same effect. This increase in dosage leads to a greater risk of addiction.
Muscle relaxer addiction can be dangerous, as it often leads to physical and psychological dependence, overdose, and other serious health consequences. Individuals struggling with addiction may experience withdrawal symptoms when they attempt to stop taking the medication, making it difficult to quit without professional help.
Recognizing the signs of muscle relaxer addiction is essential for early intervention. Some common warning signs include
If you or someone you know is showing any of these signs, it’s important to reach out for professional assistance. Early intervention can prevent the situation from worsening and help individuals regain control of their lives.
Muscle relaxer addiction treatment typically involves a combination of detoxification, counseling, and behavioral therapy. The goal of treatment is to help individuals stop using muscle relaxers, manage withdrawal symptoms, and learn healthy coping strategies for dealing with pain or stress.
In addition to traditional treatments, many addiction recovery programs offer holistic approaches that focus on healing the mind, body, and spirit. These programs may include practices such as yoga, meditation, Reiki, acupuncture, and nutritional counseling. The goal is to promote overall well-being, reduce stress, and support emotional healing, which can complement the physical aspects of recovery and improve the chances of long-term success.

If you or someone you know is struggling with muscle relaxer addiction, help is available. Prescription drug addiction treatment centers provide specialized programs to support recovery and help individuals regain control of their lives.
At Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, CA, we understand the complexities of prescription drug addiction and are here to guide you through the recovery process. Our dedicated team offers personalized care and support every step of the way. Don’t wait—take the first step toward a healthier, drug-free life. Contact us today!
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for:
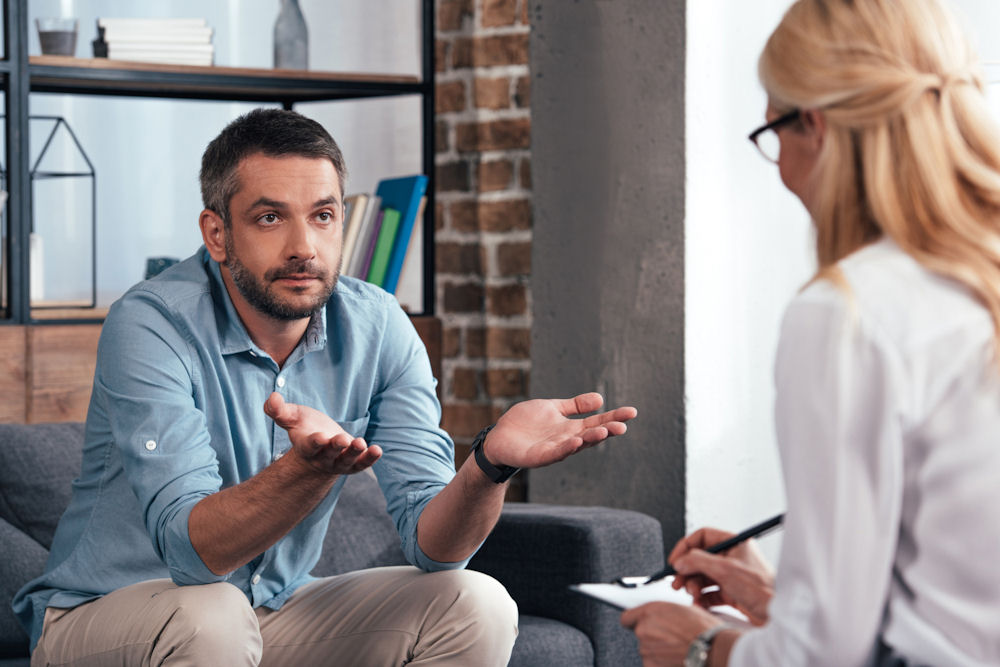

That little pill might seem like it comes and goes quickly, but clonazepam has its own schedule for leaving your system. Your metabolism, dosage, and how often you take it all influence how long traces stick around in blood, urine, or even hair follicles. This timeline matters more than you might realize, especially when it comes to drug tests, side effects, or mixing medications.
While Klonopin’s calming effects fade within hours, the drug itself lingers much longer. The half-life tells part of the story, but your body composition and liver function write the rest. Understanding these factors helps you predict when you’ll be completely clear and what to expect along the way. Let’s break down exactly how your body processes this benzodiazepine.
Klonopin, or clonazepam, is a medication that helps manage seizures and panic attacks. Klonopin is a type of benzodiazepine that works by boosting the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a chemical in your brain that naturally calms nerve activity. Enhancing GABA’s calming action allows clonazepam to reduce excessive nerve signals, which can help prevent seizures and ease anxiety.
Klonopin, along with other benzodiazepines, functions by binding to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors located in the brain and spinal cord. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter that inhibits nerve signal transmission.
By interacting with these receptors, clonazepam amplifies GABA’s effects, leading to reduced anxiety and muscle relaxation, as well as providing preventive or therapeutic benefits for seizures. However, the medication may also induce side effects such as dizziness, coordination difficulties, and mood alterations, with drowsiness being a frequent occurrence, which can be beneficial in certain situations.
People turn to Klonopin (clonazepam) for various medical reasons. Here’s a rundown of its primary uses:
After you take Klonopin by mouth, it usually starts to work within 20 to 60 minutes. The strongest effects are typically felt between one to four hours after taking it. Several factors can influence how quickly Klonopin works for you, including your metabolism, age, weight, and whether you’ve taken it with food. For instance, popping a pill on an empty stomach may make the medication absorb faster.
Klonopin operates by binding to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors, which are specific sites in the body. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter that induces a calming effect. By enhancing GABA activity, clonazepam effectively reduces anxiety and promotes relaxation throughout the body. Klonopin influences your brain and body in various ways. Here’s how it affects different systems:
Klonopin (clonazepam) is a long-acting benzodiazepine with an elimination half-life typically ranging from 30 to 40 hours. This means it can take approximately six to nine days for the drug to be fully eliminated from your system. Detection windows for Klonopin vary depending on the type of drug test used:
Klonopin (clonazepam) can cause various side effects. Here’s a rundown of some common ones:

Stopping Klonopin (clonazepam) suddenly can lead to withdrawal symptoms, especially if you’ve been using it for a while. Here’s a rundown of common withdrawal symptoms:
Klonopin (clonazepam) is a benzodiazepine prescribed for anxiety, panic disorders, and seizures. However, its potential for addiction is significant. Here’s what you should know:

Klonopin (clonazepam) and Xanax (alprazolam) are both benzodiazepines used to treat anxiety and panic disorders, but they have notable differences:
Overcoming Klonopin addiction involves a comprehensive approach tailored to your personal needs and goals. Key components of effective treatment may include:

Addiction doesn’t define you. At Golden Gate Recovery in Novato, California, you’ll never have to face recovery alone. This is a place where real support meets your unique journey. Through evidence-based therapies and genuine compassion, you’ll work with a community that truly understands your struggles and goals.
At Golden Gate Recovery, we know every journey has its ups and downs. Our drug and alcohol treatment programs meet you where you are, combining clinical expertise with real human connection. With holistic therapies and personalized care, our team walks beside you toward lasting change. When you’re ready to begin again, Golden Gate provides the tools, support, and belief in your potential to make it happen. Contact us today to begin your comeback story and move on to a healthier life.
Get confidential help! Call Us Now for: